Adrenal Gland Hormones and Functions
The adrenal glands are two organs located at the top of each kidney. These glands are responsible for producing hormones that regulate normal bodily functions.
Adrenal glands produce three types of hormones: glucocorticoids, androgens, and mineralocorticoids.
1. Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are hormones responsible for the following:
- Regulates glucose levels
- Aids in fat deposition
- Defends the body against infection
- Helps the body react to stress
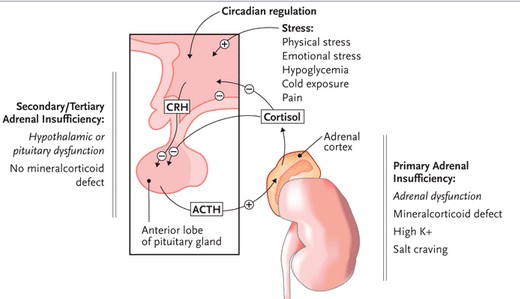
Cortisol is the main glucocorticoid in the body. Cortisol is produced by the stimulation of the adrenal gland by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) produced by the pituitary gland.
The hypothalamus produces a corticotrophin releasing hormone which stimulates the production of ACTH by the pituitary gland. In turn, ACTH produced by the pituitary gland helps the adrenal gland produce cortisol.
2. Mineralocorticoids
The main mineralocorticoid produced by the body is aldosterone. Aldosterone is the hormone responsible for regulating sodium, potassium, blood pressure and blood volume. Aldosterone promotes the retention of sodium and excretion of potassium. As aldosterone retains sodium, it also retains water which leads to increase in blood. Reduction in aldosterone production leads to sodium excretion with resulting excessive water excretion, hypovolemia, hypotension and high potassium levels.
3. Androgens
The adrenal gland also produces androgens such as testosterone, DHEA sulfate and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).
In women, androgens are produced primarily by the ovaries and the adrenal glands. Testosterone gives rise to the secondary sex characteristics of women such as growth of pubic and axillary hair. This hormone is also important for the sexual drive or libido in women.
Most androgens in men are usually produced by the testes. Because of this, testosterone produced by the adrenal glands is not as important in the sexual function of men.
What is Adrenal Insufficiency?
Adrenal Insufficiency involves the inability of the adrenal glands to produce adrenal hormones, specifically glucocorticoids (cortisol or steroid). Adrenal insufficiency may also involve inadequate amounts of mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) and androgens (testosterone). There are two classifications of adrenal insufficiency:
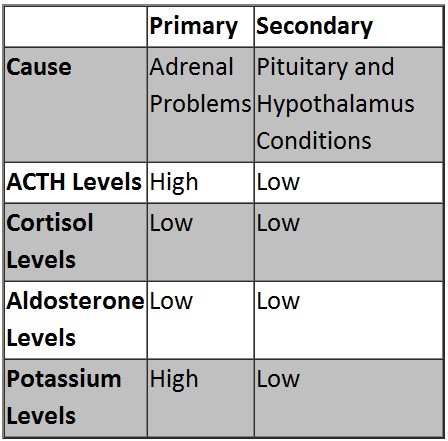
Primary adrenal insufficiency
Primary adrenal insufficiency results from inadequate production of adrenal hormones as a result of the destruction of the gland itself. Despite ACTH production of the pituitary gland, the adrenals do not respond and do not produce the right amount of hormones. The main cause of primary adrenal insufficiency involves an autoimmune disorder leading to idiopathic atrophy of the adrenal gland and a decrease in size of the gland. Other causes of primary adrenal insufficiency may include tuberculosis, fungal infection, hemorrhage and other diseases affecting the adrenal glands. It can also be due to congenital adrenal hyperplasia, cytotoxic agents or enzyme inhibitors.
Primary adrenal insufficiency may be acute or chronic and prevalence is equal between females and males. It is a rare form of adrenal insufficiency affecting .035% in every one million people.
Secondary adrenal insufficiency
Secondary adrenal insufficiency does not involve damage to the adrenal glands but an impairment of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland leading to inability of the two organs to produce hormones (ACTH or CRH) that stimulate and regulate the adrenal glands. Causes of damage to the pituitary and hypothalamus include cancer, hypothalamic tumor, pituitary tumor, head injury or Sheehan’s syndrome (impairment of the pituitary gland).
Suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary complex may also be seen in improper administration of exogenous steroids. Sudden withdrawal from steroid therapy does not allow the pituitary gland and hypothalamus to adjust, causing them to cease production of ACTH and CRH. Because of this factor, secondary adrenal insufficiency has become relatively common.
Primary and Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency is summarized below:
When the body is subjected to stress, the body is unable to adapt normally because of inadequate cortisol. As a result, adrenal crisis occurs.
Signs & Symptoms
Symptoms of adrenal insufficiency depend on the certain type of the disease although some symptoms may be similar to both types.
Primary Adrenal insufficiency
- Darkening of skin on the face, back of hands and neck
- Postural hypotension
- Light headedness when lying or standing up
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dehydration
- Salt cravings
- Muscle and joint pain
- Decrease in libido and decrease in pubic and axillary hair in women
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency
- Hypoglycemia, shaking, sweating, anxiety
- Weakness, tiredness
- Muscle aches
- Palpitations
- Darkening of skin is not present
- Dehydration does not occur
- Nausea and vomiting is less common
Presence of tumor in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland may also include the following symptoms:
- Headache
- Impaired peripheral vision
- Infertility
- Impotence
- Hoarseness
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Short stature in children
- Delayed puberty
Causes
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency
Causes of primary adrenal insufficiency include:
- Autoimmune disease (such as autoimmune adrenalitis)
- Infection (Fungal infections, Tuberculosis, AIDS, etc.)
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Tumor of the adrenal gland
- Hemochromatosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Accidental removal of the adrenal gland as a result of kidney surgery
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency
- Causes of secondary adrenal insufficiency include:
- Tumor of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland
- Head injury
- Craniopharyngioma (benign tumor that damages the pituitary gland)
- Sudden withdrawal of long-term steroid therapy
Diagnosis
Diagnosing adrenal insufficiency involves several tests to determine the extent of the condition, the type, and identify the underlying cause. Diagnostic tests include:
Cortisol Level testing
Blood sample is collected from a patient early in the morning. A very low result may indicate adrenal insufficiency. A very high level of cortisol may indicate Cushing’s disease (overproduction of adrenal hormones).
ACTH Stimulation Test
This test ascertains the presence of adrenal insufficiency and establishes a primary adrenal insufficiency. The cortisol level is usually measured and then high doses of ACTH are administered through the vein. A blood sample is again collected after 60 minutes. A very low level of cortisol, despite the administration of ACTH, indicates primary adrenal insufficiency.
ACTH level Testing
ACTH level testing also determines if the problem is primary or secondary adrenal insufficiency. A high ACTH level indicates primary adrenal insufficiency and a low ACTH level indicates secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Determining the underlying cause
In order to determine the underlying reason for the insufficiency, series of tests are done such as:
- Chest X-rays to determine tuberculosis
- Abdominal CT scan to check the adrenal glands for any defect
- MRI of the cranium to determine tumors in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
- A detailed medical history is also obtained to determine medication use including steroids or cytotoxic drugs.
Treatment
Treatment of adrenal insufficiency is usually successful. Early detection is essential for prompt treatment when complications are not yet present. Treatment also involves lifelong duration of hormonal therapy to normalize adrenal hormone levels. It also depends on the type of adrenal insufficiency.
Primary Adrenal insufficiency
Treatment of primary insufficiency involves administering exogenous glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid for life. Androgen is also given to women. Proper administering of hormones is necessary to prevent high levels that may lead to Cushing’s syndrome.
Glucocorticoid Therapy
Prednisone is one of the most common exogenous glucocorticoid given to patients. However, other steroids such as Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone and dexamethasone may also be used.
Monitoring during treatment is important to assess rapid weight gain and puffy face because it usually indicates over-dosage of the steroid. Over-dosage may potentially lead to over-thinning of the bones. Dosage is usually tailored to the body weight of the patient. Obese patients may need higher doses and children and elderly may require lower doses.
Mineralocorticoid Therapy
Mineralocorticoid therapy includes the use of Fludrocortisone Acetate (Florinef), an oral synthetic mineralocorticoid. The administration of the drug is monitored by regularly checking the blood pressure and potassium levels. Over-dosage may lead to hypertension and hypokalemia because of increase in retention of sodium and water.
Androgen Therapy
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is given daily to women to improve libido and over-all sense of well-being. Men do not require androgen therapy because the testes still functions in the production of testosterone. Side-effects include acne, a deepened voice, and facial hair associated with elevated testosterone levels.
Intravenous fluids may also be given to address dehydration.
Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency
Secondary adrenal insufficiency only needs glucocorticoid replacement because production of mineralocorticoid and androgen is usually not affected.
Complications
Prognosis of treated and monitored patients is usually good. Most patients have a normal life and an average life expectancy. Children who are treated can also experience growth and puberty without any problems. Complication of untreated adrenal insufficiency includes adrenal crisis as manifested by severe abdominal pains, diarrhea, vomiting, fatigue, profound muscle weakness, depression, confusion, marked hypotension, fever, kidney failure, weight loss, and shock which may lead to death.
Adrenal crisis is a life-threatening condition that occurs because of exposure to infection, trauma and other forms of stress. Adrenal crisis requires an emergency medical treatment. An emergency injection of glucocorticoid should be given. Family members or caregivers should be taught to administer injections of glucocorticoids at home in case of adrenal crisis. Emergency measures also include administering of intravenous fluids in bolus to treat severe dehydration. Mineralocorticoids are also given once the patient is stable. The underlying cause is also treated to prevent another adrenal crisis.
Patients are taught the signs and symptoms of adrenal crisis for early detection and management.
Precautions:
People with adrenal insufficiency should have a medical alert bracelet to ensure proper management during emergency situations. They should also have an information card listing the medications and doses, including contact person during emergencies.