Cat Scratch Disease – Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis
What is Cat Scratch Disease?
It is a disease that is caused by the infection of Bartonella bacteria which is transmitted by cat bites and scratches. It is abbreviated as CSD and it is otherwise known as Cat scratch fever or Bartonellosis. The bacteria live in the cat’s saliva and may have the tendency to carry if for a couple of months or so until it spreads to others via physical contact. The person, who has the disease condition, usually complains of having a history of being bitten or scratched by a cat, most often a kitten. Studies show that young cats, specifically kittens, are often the ones to carry such bacteria compared to older cats. Also, household kittens are the high rates of acquiring the infection. The rate becomes higher if the cats have a presence of fleas. It is self limited and common syndrome. It may otherwise be due to lick, bite or scratch of the cats. Children are often the targeted persons or the persons who often have this kind of disease condition.

Cat scratch disease commonly results from a cat scratch or bite
Cat Scratch Disease Symptoms
Persons who are known to have this kind of disease condition are known to manifest the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Body malaise or discomfort all over
- Tender regional Lymphadenopathy or swelling of the lymph nodes which develops around 1-2 weeks after the scratch or being bitten by a cat or kitten
- Low Grade Fever
- Pustule or blister
- Enlarged spleen or spleenomegaly
- Papule or bump which is otherwise known as inoculation lesion
- Weight loss which is unexplained
- Sore throat
- Losing of appetite
- Rashes
- Crusting of the pustule may also occur
- Anorexia
- Nausea
When the following symptoms occurs:
- Seizure
- High fever
- Mental status changes
- Level of consciousness changes
It may indicate a condition which is life threatening and there is a need to seek medical help immediately to prevent further complications.
Cat Scratch Disease Diagnosis
Most often the persons who have cat scratch disease do not recall their experience of being bitten or scratched by a cat or a kitten. Hence, it is important that they undergo test to be able to confirm the suspected diagnosis, which is cat scratch disease. Such examinations that one must undergo are as follows:
- Physical examination which may reveal that their spleen is enlarged
- Bartonella Henselae IFA test is an accurate and confirmatory diagnosis of this kind of disease condition
- Lymph node biopsy and Blood culture is done to be able to rule out the other etiology of the swelling of the person’s glands
- Microscopic Exam from the affected swollen lymph node may also be done
These are the common diagnostic test that is associated with the confirmation of this disease condition.
Cat Scratch Disease Treatment
Actually persons who are diagnosed with Cat Scratch disease does not entirely need treatment whatsoever unless the person has symptoms that are systemic in nature or there is a presence of adenopathy. The common treatments used for this kind of disease condition include:
-
Pharmacological Medication
Antibiotics are the medications often given to eradicate the bacteria that cause this disease condition. Antibiotics may vary depending on the individual’s reaction to such. The following are the suggested antibiotics used for persons who have cat scratch disease:
- Azithromycin
- Rifampin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Doxycycline
- Gentamicin
- Erythromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Sulfamethoxazole
- Trimethoprim
Aside from antibiotics, one can take pain relievers such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen. One should take note that, aspirin should be avoided especially with children.
-
Moist Compress
It can be given to a child or the patient to be able to ease the soreness of the nodes.
-
Lymph node Aspiration
It may only be required when there is a presence of suppuration. The use of aspiration may be considered to be as a therapeutic as well as a diagnostic approach. When a person reports of recurrent pain and pus reaccumulation, there may be a need for repetition of aspiration procedure.
-
Surgical Excision
It is done especially if the person has already a presence of an enlarge nodule which may be indicated when there is a continuous repetition of aspiration and still fail to relieve the pain that the person reports to have. The physician may suggest excising a persistent granuloma.
Cat Scratch Disease Prevention
This kind of disease condition happens rarely. Since the cause of this disease are mainly because of physical contact with cats, the main prevention of such is to avoid dealing with cats specially those that are stray and those that has fleas on it. If you are keeping a pet cat in your house, there is a need for you to be responsible enough to have regular visits to the veterinary and to make sure, as much as possible, that they do not acquire fleas by keeping them clean. You need to have an open communication with your veterinarian so that you will be guided to the right treatment or product to use for your pet cats. Also, in addition to that, is that children are the often the common victim of this kind of disease condition. Hence, as young as they are, they must be taught to handle their pet cats gently and appropriately to prevent such disease to occur. The child should not in any way provoke or tease the cat so as to prevent the cat from biting or scratching them. They can do by telling them to wash thoroughly their hands after touching or playing with any cats. If in any instance, the child had been bitten or scratched by a kitten, there is a need to consult a trusted physician to help deal with such matter on hand. Also, the first aid to do, when a child or a person is scratched or bitten by a cat, is that you need to wash it off by the use of running water and soap.
Cat Scratch Disease Pictures
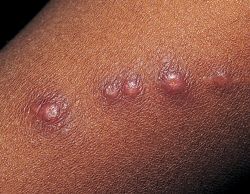
Papule or bump which is otherwise known as inoculation lesion
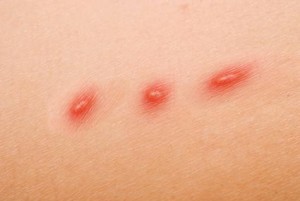
Pustule or blister in cat scratch disease 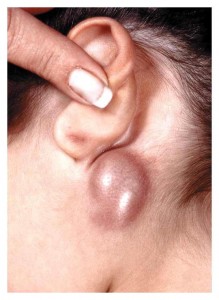
Swollen lymph nodes as commonly seen in CSD