Ocular Rosacea – Pictures, Treatment, Symptoms, Causes
What is Ocular Rosacea?
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition where there is formation of papules on the face as well as appearance of thin blood vessels under the skin. Rosacea affects 5% of the world population with increased risk for people in the middle adulthood stage. Women and fair-skinned people also have a higher risk for developing it.
Rosacea is sometimes linked to the occurrence of acne; however, acne and rosacea are different. Rosacea often involves the eruptions of tiny papules on the skin, especially on the face. Causes of rosacea include skin mites, Pitorosporum ovale and other fungal and bacterial infections. Connective tissue problems, gastric secretions and genetics also play a role in the development of rosacea.
Symptoms of rosacea include the appearance of a rash on the nose and face, frequent blushing, telangiectasia or appearance of small capillaries on the face, firm acne nodules, and pustules on the face.
When rosacea is not managed accurately and promptly, it usually leads to complications. Ocular rosacea is one complication of a rosacea disorder when the condition is left untreated. It affects 20% of those having facial rosacea. It involves the affectation of the eyes and eyelids and may cause a burning sensation in the area. It is similar to seborrheic dermatitis, affecting the eyes because it leads to a chronic inflammation of the eyelids with resultant crusts and scales. Some also experience the occurrence of rhinophyma or a bulbous nose as a result of rosacea.
Symptoms and Signs of Ocular Rosacea
Ocular rosacea produces symptoms such as:
- Redness of eyes or blood shut eyes
- Irritation
- Burning sensation
- Feeling of having an eyelash on the eye
- Gritty feeling on the eye
- Swollen eyelids
- Small bumps on the eyelids
- Falling of eyelashes
- Photophobia
- Pain on the eyes
- Dryness of the eyes
- Blurred vision
- Appearance of stye
- Evident small blood vessels on the sclera or the white portion of the eyes
The symptoms of ocular rosacea are usually distinct from the severity of skin rosacea. Other complications include the following eye conditions:
- Conjunctivitis or the inflammation of the bulbar conjunctiva
- Blepharitis or inflammation of the eyelids
- Iritis or the inflammation of the iris
- Keratitis or the inflammation of the cornea
- Iridocyclitis
- Hypopyoniritis
Causes of Ocular Rosacea
The exact cause of ocular rosacea is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development. The focus of the risk factors includes becoming dehydrated and eye irritation as a cause of ocular rosacea. Causes of ocular rosacea are synonymous to the causes of facial rosacea which include:
- Consuming high amounts of beverages containing caffeine
- Drinking alcoholic beverages
- Eating spicy foods
- Exposure to extreme temperatures
- Prolonged exposure to the sun
- Stress
- Strenuous exercise
- Frequent hot baths or sauna baths
- Some antihypertensive medications
- Corticosteroid therapy.
- Family history of rosacea and being fair-skinned also contribute to the occurrence of ocular rosacea.
Treatment of Ocular Rosacea
The management of rosacea is focused on alleviating the symptoms and eradicating the causative factors. Managements include:
Warm compress. Warm compresses may be placed on the eyelids and eyes to relieve pain and irritation. A warm compress also liquifies the thick secretions in the meibomian gland, located on the eyelids, which enhances excretion.
Washing eyes with warm water. Good eye care is essential in removing the crusts and allowing the area around the eyes to be moisturized. Other mild cleansers may be used to clean the eyelids. Gentle pressure on the eyelids may also help in expressing the thick secretions.
Artificial Tears. Artificial tears aid to relieve dryness in the eyes. Non-preserved artificial tears are used during the day and lubricating ointment may also be applied at night.
Antibiotics. These drugs are used to counteract and prevent eye infection. Antibiotics are in the form of tetracyclines, erythromycin or doxycycline. Metronidazole may also be given to aid in the management of ocular rosacea through its anti-inflammatory property. Antibiotics should be taken as prescribed to prevent drug resistance. Patients with asymptomatic ocular rosacea who do not manifest severe ocular rosacea should not be given antibiotics.
Steroids. Topical corticosteroids are used for acute exacerbation of the condition. This relieves inflammation associated with keratitis and other inflammatory conditions of the eyes. However, the use of topical steroids should be monitored because it can lead to corneal melting after prolonged use.
Retinoids. Retinoids or Vitamin A derivatives can be used to reduce inflammation in the eyes associated with ocular rosacea. It is very helpful in the prevention of over-secretion of sebum by reducing the size of sebaceous glands. The most commonly used retinoids are tretinoin and isotretinoin. However, these compounds should not be used during pregnancy because they cause teratogenic effects to the fetus, leading to congenital anomalies.
Immunomodulators. Immunomodulators such as cyclosporine are used for anti-inflammatory action that reduces secretions in the eyelids.
Anti-ulcer drugs. The use of anti-ulcer drugs is necessary for the treatment of ocular rosacea because the occurrence of ulcer has been linked to the development of rosacea.
Dietary Restrictions. Dietary restrictions are also essential, especially in the treatment of mild forms of rosacea. This includes avoidance of irritating foods such as alcohol, spicy foods, hot beverages, and caffeine. Diet is one of the causes of rosacea; thereby, restricting a person’s intake of these foods is very important.
Sun protection. When going out, patients with ocular rosacea should protect the eyes from the sun by using sunglasses, an umbrella or a cap to reduce the harsh effects of the sun.
Surgery. More severe cases of ocular rosacea require surgery to correct the condition. Punctual occlusions may be helpful to prevent excessive secretions. Amniotic membrane may also be used to reconstruct the damaged cornea in cases of corneal ulceration or epithelial defect. Keratoplasty and limbal system transplant is also done for corneal ulceration and limbal system deficiency.
Prevention of Rosacea
Once facial rosacea has occurred, it is difficult to prevent rosacea. However, early management of facial rosacea is very essential to prevent its development. Other measures that can be done include:
- Comply with the treatment plan even if symptoms of facial rosacea have already resolved.
- Avoid things that potentially trigger the development of ocular rosacea such as preventing extremes of temperature, irritating foods, caffeine, exposure to the sun, and alcohol consumption.
- Avoid using contact lenses for the moment until facial rosacea has been treated completely.
Pictures
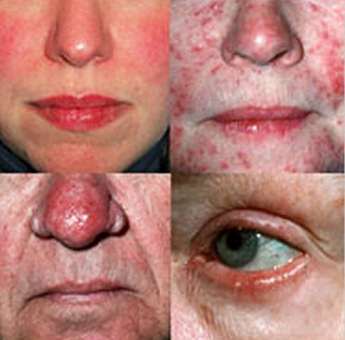
Picture 1 – Four forms of rosacea
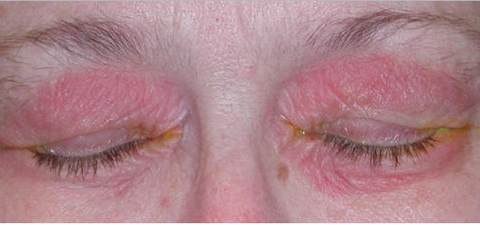
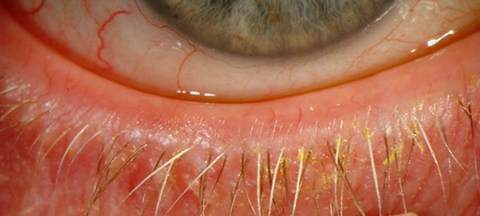
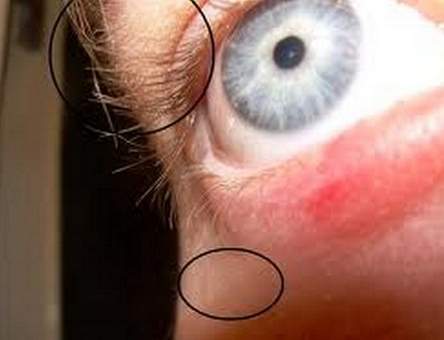
Image source – gstatic.com
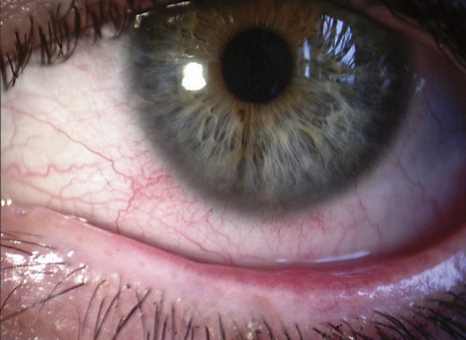
Picture 5 – Ocular, Eyelid involvement in Ocular rosacea
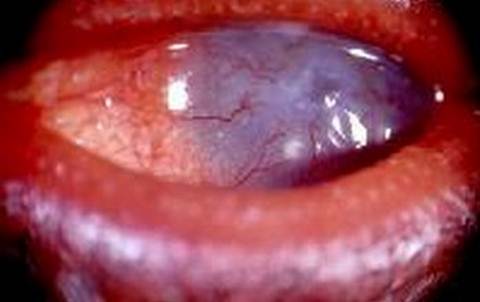
Picture 6 – Excessive pannus and corneal thinning in ocular rosacea