Panniculitis – Pictures, Treatment, Symptoms, Types, Causes
Panniculitis Definition
Panniculitis is a subcutaneous fat disease and inflammatory disorder affecting the skin. The fatty layer of our skin is the main area of affectation, leading to an inflamed skin. Swelling of the skin is noted and mostly observed in the patient’s abdomen (considering the subcutaneous layer is thick in this area). The skin becomes inflamed and elevation of red spots or noticeable nodules is also observed. The condition not only affects humans but is also reported among animals such as cats and dogs.
Classification (Types) of Panniculitis
a. Mesenteric
The mesenteric panniculitis is characterized by the fatty degeneration of the abdominal cavity. There are about 300 noted cases of mesenteric panniculitis. This condition is quite common in males and is said to greatly affect Caucasian people. Old age is also considered as a factor for mesenteric panniculitis but this does not leave the young unaffected. This classification of panniculitis is said to be idiopathic in cause or from an unknown root.
b. Lupus
Lupus panniculitis is attributed from a variant of lupus erythematosus and is considered a rare type of panniculitis. The disease involves fatty tissues and most cases are acquired due to the underlying discoid form of lupus erythematosus. The classification is also known as lupus erythematosus profundus. The condition is most common in adult women and is characterized by the development of multiple nodules on the proximal extremities and trunk. This classification is known to cause scarring that leaves traces of lipoatrophy – a localized fat tissue loss. Lupus panniculitis also considered a complication of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
c. Septal
Septal panniculitis or vasculitis septal panniculitis is a rare type of panniculitis. This is variably linked to a systemic reaction that leads to vasculitis – blood vessel eruptions. The skin lesions are reddish in color. There shall be darkening of the skin as the lesions heal. It is quite distinct from the other types of panniculitis as this can cause fever, joint pains, and generalized body malaise.
d. Lobular
The lobular panniculitis was also known as the Weber-Christian disease. This type of panniculitis is known to manifest recurrent multiple tender nodules in the subcutaneous fat. This condition is caused by a form of trauma or occurs in people who are not properly insulated from cold weather. The condition is also now referred to as the relapsing febrile nodular panniculitis. This type of panniculitis is characterized by the development of bruising plaques on the skin, mainly in the arms and thighs. Those affected of such classification are young men.
e. Pancreatic
This is another rare type of panniculitis, just like lupus panniculitis. The condition is only possible when there is an underlying pancreatic disorder. The mechanism of the disease is activated by lipase (activated pancreatic enzyme), phoplipase, trypsin and amylase. These pancreatic enzymes are found to affect the blood vessel wall thus inducing necrosis and inflammatory skin lesions.
f. Sclerotic
This classification of panniculitis is not quite understood. The condition arises and is defined by the development of unsmooth skin surfaces (where lesions have developed) and pain on the area upon palpation. This type of classification is not considered serious compared to others.
g. Necrotizing
Necrotizing panniculitis arises when there are necrotic spots emerging from the lesions. This is characterized as very painful, especially when touched. This type of panniculitis is also disabling and debilitating in nature. It is considered necrotizing when there is tissue breakdown involvement.
Panniculitis Symptoms
The panniculitis, as already mentioned, is a skin disease that affects the subcutaneous fatty layer and/or abdominal layer of the skin. The following are the associated symptoms of panniculitis:
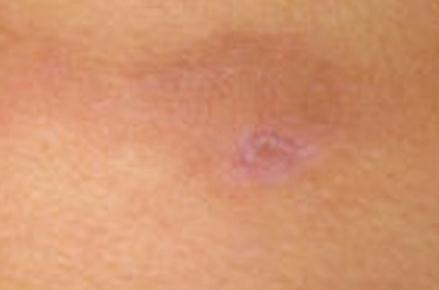
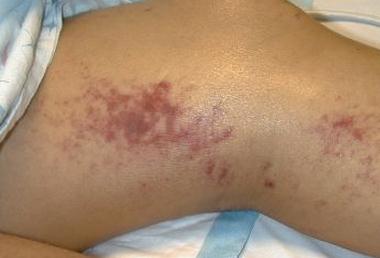
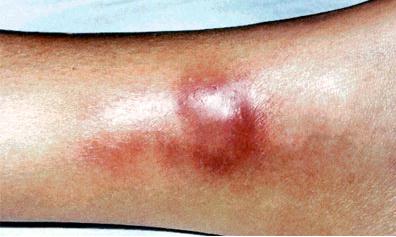
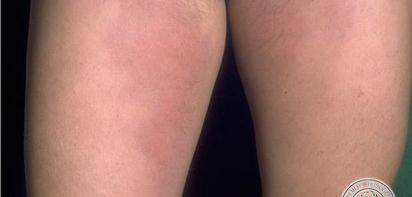
- Firm and painful lesions are observed. The lesions are identified in nodules which compose about 35% of the affected area. These nodules are found prominently in the abdomen, but not sparing the ventrolateral neck and chest areas. The nodules are also found to be deep in characteristic.
- Rupture of the nodules is possible. There shall be oil draining from the nodules which are yellow-brown to bloody in presentation.
- Weight loss is one manifestations. The client tends to lose weight due to the systemic affectation of the disease. There are multiple organs involved with this condition and tissues such as the subcutaneous fat are involved.
- The patient tends to become easily fatigued. This increased tiredness is due to the pain and discomfort that comes with the condition.
Panniculitis Causes
The following are the possible causes of panniculitis:
- Trauma. If injury has been incurred on the skin, specifically the subcutaneous fatty layer of the skin, the development of such conditions is possible, especially when one has an underlying pancreatic problem. Certain traumas are highly causative of panniculitis. These are IV injections, cryosurgery, and rigorous exercise.
- Underlying condition. It has been noted that diseases which involve the connective tissue cause panniculitis. Lupus and scleroderma are known causes of the disease. Pancreatitis is also considered one of the underlying conditions that result in panniculitis.
- Extreme cold temperature. This is considered a cause whenever there is injury done via contact with extreme cold objects or temperatures. The injury can become or develop painful nodules. Newborns are affected when hypothermia (decreased body temperature) is experienced during childbirth.
- Alpha 1 deficiency. This is considered to bring about the skin problem. There are a number of cases where Alpha 1 deficiency has caused panniculitis.
Diagnosis of Panniculitis
The following are the considered tests for panniculitis:
- Physical examination of the client’s skin would assist in the diagnosis of the disease.
- The condition can be readily identified if the patient undergoes a skin biopsy. This shall present necrotic components of the skin’s surface or the subcutaneous fatty layer. A hispatopathology examination of the skin can confirm panniculitis.
- Imaging of the abdominal wall would also help in evaluating the skin problem. This can be attained through an ultrasound-guided biopsy, and radiographic tests would also provide a clear picture of the affected area.
Treatment of Panniculitis
Treatment for panniculitis is aimed at finding a cure of the underlying condition causing the disease. The following are the proposed conventional treatments for panniculitis:
- Provide rest. This can enhance the immune system and avoid aggravating the condition.
- Provide anti-inflammatory medications. This is very helpful in the process as this can lower swelling and pain experienced by the affected. Medications such aspirin and ibuprofen are provided to patients.
- Steroids are given to patients in oral or intravenous forms. This can lessen the inflammation that worsens the disease.
- Antibiotics are also found helpful in treating infections and also to avoid development of infections.
- Surgery. When the lesions are in a grave state and necrosis and ulcerations have developed, surgical treatment is to be provided. Scraping off the necrotizing tissue is done to avoid spreading.
Panniculitis Pictures
Below are the images, photos of panniculitis