Polyps in Uterus – Symptoms, Causes, Removal, Treatment
What are Polyps in the Uterus?
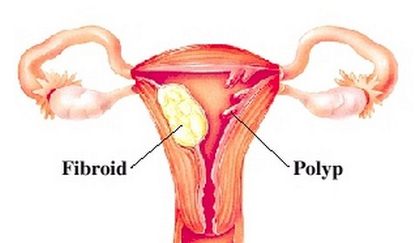
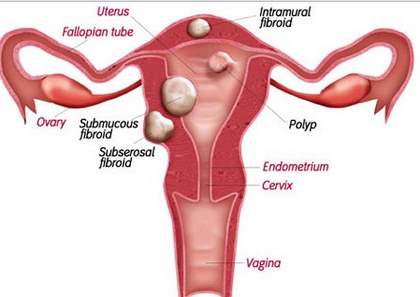
Uterine polyps, polyps in uterus or endometrial polyps are tissue over growths in the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus responsible for menstruation. During menstruation, the endometrium sloughs off and become menses. After it, the endometrium proliferates in preparation for possible pregnancy. When the endometrium over proliferates, it may cause the development of uterine polyps. These over growths are small, round, bulb-shaped outgrowth from the endometrium and are attached to the womb by a stalk. Uterine polyps are soft in contrast to uterine fibroids which are hard and bigger.
Uterine polyps are usually asymptomatic, however, when symptoms appear, these are similar to the symptoms of endometrial cancer, a more serious condition. Uterine polyps are generally benign, but less than one percent of cases are associated with uterine malignancy.
Most women had experienced uterine polyp for some time, but has resolved spontaneously. Uterine polyp is considered a mild condition and some patients are even asymptomatic, which makes them unaware of the uterine polyp. Uterine polyps commonly grow during the pre and post menopausal age.
Picture – Fibroid and Polyp in Uterus
Image Source – women-health-info.com
Uterine polyps Symptoms
Symptoms of uterine polyps include:
Abnormal uterine bleeding that may be:
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Spotting in between menstruation
- Heavy menstruation
- Bleeding after menopause
Grows up to a size of sesame seeds and golf ball
May be single or multiple
Some are asymptomatic
Uterine polyps may be mistaken for uterine fibroids or myoma. They are both hormone induced and may have similar symptoms. Here are the most common differences of the two:
Difference between Uterine polyp and Uterine Fibroids
| Characteristics | Uterine Polyp | Uterine Fibroids or Myoma |
| Size | Relatively small | May grow up to the size of a watermelon |
| Composition | Made up of endometrial tissue, soft and malleable | Made up of hard muscle tissue, which makes it tough |
| Regression | Polyp may regress in some point | Do not regress |
What causes polyps in the uterus?
The exact cause of uterine polyps is unknown, but is associated with the reduction of estrogen levels in the body. Risk factors include:
- More than 40 years of age
- Undergoing the pre-menopausal stage or already experiencing menopause
- Previous intake of anti-estrogen medications such as tamoxifen
- Obesity with more than 30 body mass index
- Presence of hypertension
- Use of hormone replacement therapy
Diagnosis of Uterine Polyps
The diagnosis of uterine polyps is made using the following procedures:
- Hysterosalpingogram – This involves the injection of contrast medium inside the uterus and fallopian tubes. X-ray images are taken to determine any obstruction of uterine polyps inside the uterus. The contrast medium is usually iodine based so patients should be assessed for allergies to seafood.
- Hysteroscopy – This employs the insertion of thin tube with a camera on the tip, which allows the gynecologist to examine the uterine cavity and locate the presence of polyps. The size is also accurately identified using this procedure. An instrument may also be inserted during the procedure to remove the polyp in the uterus.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound – This procedure employs the insertion of an ultrasound sensor in the vagina to accurately get an image on the inside portion of the pelvis.
- Sonohysterogram – Sonohysterogram employs the use of ultrasound plus the instillation of normal saline solution in the uterus to make a balloon-like organ. This allows for undetected polyp to be seen.
- Biopsy – Biopsy is done to determine any presence of malignancy. This is the most definitive test to identify malignancy in the uterine polyp.
Treatment of Uterine Polyp
Uterine polyp may eventually disappear after some time; however, when there is excessive bleeding and affectation of fertility, these are electively removed. Treatment for uterine polyp is commonly done through surgical removal of the tumor. These include:
Curettage
Curettage involves the scraping of the uterine wall to remove endometrial polyp. This uses a special instrument called a curette to effectively remove the outgrowth. Curettage is usually guided by hysteroscopy. Dilatation and curettage may also be applied, which does not involve the use of hysteroscopy. The gynecologist should be knowledgeable on the locations of the polyp to adequately remove them using dilatation and curettage.
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus when multiple polyps occur with indications of malignancy. The uterus is removed from the pelvic cavity and the cervix may be preserved. Other organs such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes and cervix may also be removed when malignant cells are also present. However, uterine polyp seldom progress to cancer.
Medications
Hormonal preparations such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are given to decrease the size of uterine polyps for easier removal. Progestins may also be given for similar actions. These medications provide short-term management and the polyps may grow back after stopping the medications.
Prognosis of Uterine Polyps
Uterine polyps are considered mild and are highly treatable. Presence of abnormal vaginal bleeding should be referred to a gynecologist to prevent hemorrhage and hypovolemia. Only few conditions eventually lead to endometrial cancer when other risk factors for cancer are present.
Complications of Uterine Polyps
Complications of uterine polyps include:
Infertility – The presence of uterine polyps can lead to infertility because of the inability of the fertilized egg to implant in the endometrial layer. Polyps can also block the opening of the fallopian tube from the uterus preventing the sperm cells to meet the egg cell for fertilization. In addition, polyps can also block the cervix and prevent entry of sperm cells in the womb. Women who undergo surgical removal of the polyps usually become pregnant after some time.
Miscarriage – Pregnant women may also suffer from miscarriage after in vitro fertilization. The polyp may take the space of the fetus especially when it grows big of up to the size of an orange. However, other cases of polyps disappear following delivery.
Prevention of Uterine Polyps
Prevention involves the avoidance of modifiable risk factors. Preventive measures include:
- Management of weight o prevent obesity
- Proper diet
- Limiting salt and fat intake
- Proper management of hypertension