Groin Hernia – Pictures, Symptoms, Surgery, Recovery, Repair
What is Groin Hernia?
Groin hernia, according to statistics occurs to about 4.4 percent in children and about 98 percent in children that ages 13 years old and below. Most of the children that are inflicted with groin hernia have indirect form of groin hernia which is approximately 99 percent than that of direct groin hernia which accounts for about 1 percent only.
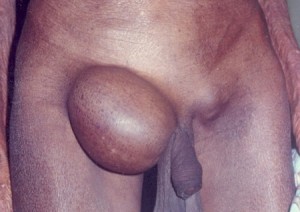
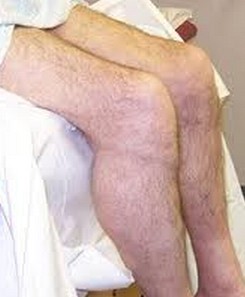
Groin hernia is actually a bulge found in the external portion of the person’s groin. It occurs when there is a spot that is weak which is found in the wall of the abdominal area. It is known to contain connective tissue, intestinal portion as well as fat. There are actually two types of groin hernia which are femoral and inguinal hernia. The groin hernia is interchanged with the inguinal hernia which accounts mostly common hernia that happens in adults.
Groin hernia showing protrusion in the groin
Groin Hernia Symptoms
-
Groin Hernia in Men
According to research and statistics, groin hernia occurs mostly on men than on women. Approximately in America alone, 500,000 men or more each year undergoes surgical repair of their hernia. Groin hernia in men occurs when the intestinal loop enters in the person’s inguinal canal which is located in the groin area which anatomically speaking is located just in between the person’s pubis and the leg’s top portion. It occurs most commonly in men who are known to do the heavy works such as picking up objects that are heavy without the use of proper body mechanics. The common groin hernia type that occurs most in men are inguinal hernias.
-
Groin Hernia in Women
The type of groin hernia that occurs in women is femoral hernias. This kind of groin hernia happens to women because anatomically speaking the women is known to have a bone structure that is wider compared to the men. The femoral hernia, which is a type of groin hernia, is not that commonly reported. According to statistics, it occurs for about 3 percent than all other hernias combined. There are five kinds of groin hernia that occurs in women such as:
-
Strangulated groin hernia in women
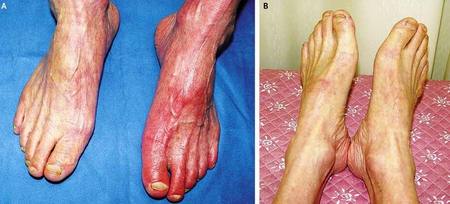
This occurs when the groin hernia will produce a blockage of the supply of blood towards the bowel part. This kind of hernia is a medical emergency kind. This may also occur in men.
-
Obstructed groin hernia in women
It happens when an intestinal part is intertwined with hernia leading to the obstruction in the intestinal portion. This may grow and may be very painful as it progress. In worst case scenario, vomiting can happen.
-
Irreducible groin hernia in women
This occurs when the hernia, particularly the femoral hernia, is stuck in the femoral canal which results in the experience of pain and illness feeling.
-
Reducible groin hernia in women
It occurs when the hernia can be push normally back into the person’s abdomen either via manipulation or done spontaneously. This kind of groin hernia is a painless kind.
-
Incarcerated groin hernia in women
Incarcerated groin hernia is a medical term that means obstructed form of hernia that can be irreducible but not really strangulated kind.
Groin Hernia Causes
When a person has tears or weakness in his or her abdominal wall it can lead to the person to have groin hernia which may be due to the following etiological reasons such as:
- Previous surgical procedure done
- Weakness of the abdominal wall which is age related
- Defects during birth
- Wear and tear that is prolonged and situational such as coughing or straining that is lifting
Groin Hernia Diagnosis
In diagnosing groin hernia, the physician usually does the following diagnostic tests such as:
- Physical examination
- Medical historical examination
- Ultrasound examination
- Computed Tomography scan examination
- X-ray examination
Groin Hernia Treatment
Usually, groin hernia will not require treatment. Yet, those persons with groin hernia that leads to the production of symptoms that leads to the enlargement of the groin hernia itself needs to be corrected or repaired by a licensed surgeon. The following treatments are done to persons with groin hernia:
-
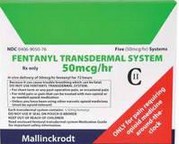
Supportive device
Prior to the surgical procedure, the person with groin hernia are expected to use truss, which is a supportive device that is worn to provide pressure on the hernia area and keeps control of the hernia itself.
-
Non surgical treatment
Non surgical treatment can be another form of treating persons with groin hernia such as:
- Weight loss
- Sleeping with the upper most pat of the body being propped up
- Don’t eat before lying to bed
- Stop smoking
- Eating fiber rich foods
- Being able to properly lift things
-
Surgical procedure
The effective and safest way of treating groin hernia is done via surgical procedure. The type of surgical procedure done will be made via the assessment of the physician in charge. It may be done via open approach, herniorrhaphy, bowel resection, hernioplasty or via laparoscopic approach.
Groin Hernia Repair
Groin hernia repair is done via surgery. The following surgical repairs commonly done by surgeons are as follows:
-
Laparoscopic surgical repair
In this procedure, the surgeon usually does small incisions in the person’s abdomen and will then inflate the abdomen via a gas that is harmless in nature. After which, the laparoscope is inserted. A laparoscope is an instrument that consists of surgical instruments and minute video camera. The long term rate of success with this surgical repair procedure is less compared to that of the open surgical repair. The advantage of this surgical repair procedure is that it heals quickly with lesser pain associated.
-
Open surgical repair
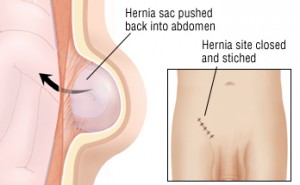
This kind of surgical repair is done via local or general anesthesia. What happens in this surgical repair is that an incision is made in the person’s groin and a small synthetic mesh material reinforces the area of groin hernia is used to prevent hernia from coming back or producing another one.
Groin Hernia Recovery
Hernia in groin which is usually treated surgically, will recover around a week or two. Hence, certain things should be done to ensure the recovery of the person who was surgically treated from inguinal hernia. The following things should be considered under groin hernia recovery:
- Healthy diet which is high in fiber, rich in vegetables and fruits
- Prevention of lifting heavy things for at least a month or so
- Pain relievers are taken for pain episodes
- Rest periods are provided
By doing such things, recovery for persons with hernia in groin will be achieved.
Groin Hernia Pictures
Supportive device used to reduce pressure on the hernia
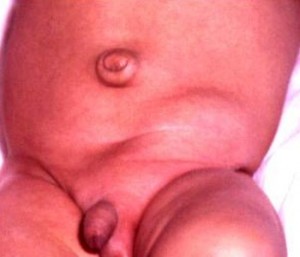
Inguinal hernia in an infant
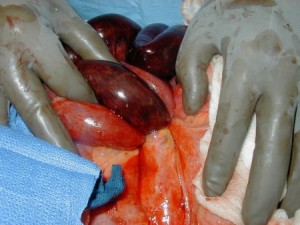
Strangulated hernia showing gangrenous bowels
Hernia repair