What is Sodium?
Sodium is an element known in Latin as natrium with a chemical symbol of Na. Elemental sodium is a supple, whitish alkali metal. Sodium is abundant in substances such as sodalite, feldspars and rock salt. Sodium also dissolves easily in water, which is why it is abundant in bodies of water, the oceans, in the form of sodium chloride.
Sodium is very essential to the human bodily processes and considered a major macro-mineral needed by the body. Sodium usually enters the body in the form of sodium chloride or salt.
Other sources of sodium are from processed foods due to the presence of sodium chloride as a preservative. The recommended daily intake of sodium is 500 mg to 2000 mg to prevent sodium-related diseases such as hypertension.
Sodium Functions
Sodium is the most common cat-ion (positively charged electrolyte) in the extracellular space in the body and accounts for almost 80 to 90% of the total sodium inside the body. It is important in regulating body processes such as:
- Blood volume
- Blood pressure
- Blood pH
- Promotes osmotic stability of cells
Sodium normally attracts water which means that any increase in sodium in the body leads to water retention as well. Aside from the water regulation in the body, the electrolyte also stabilizes nerve impulses in neurons. The nerve impulse transmission depends on the sodium availability on the cell membranes. In short, sodium is very essential for the normal functioning of cells.
What is Hyponatremia?
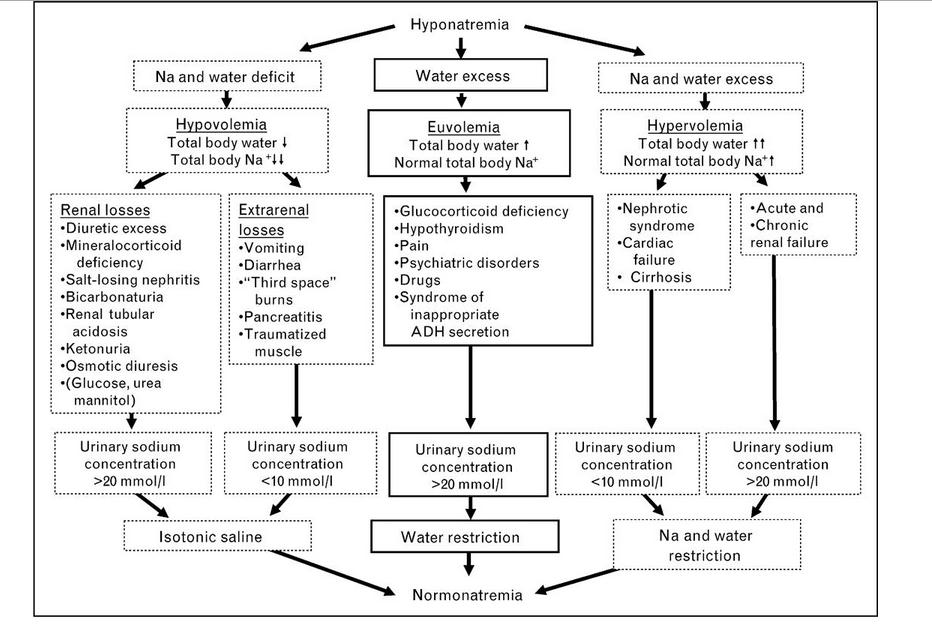
Hyponatremia is a condition wherein the sodium level in the extracellular space or in the blood is below normal. The normal sodium blood level is 135 to 145 mEq/L. Any reduction in these levels of less than 135 mEq/L affects homeostasis.
Hyponatremia is not a disease itself, but often a result from certain medical conditions that affect water and sodium levels in the body.
Hyponatremia is often caused by conditions that significantly increase water in the body, resulting in a diluted blood concentration of sodium. Limited dietary intake of sodium has never been a factor in the development of hyponatremia in healthy individuals. Although a low serum sodium can also lead to volume depletion indirectly.
Sodium being the most abundant cat-ion in the body causes hyponatremia to be the most common electrolyte imbalance. Incidences are greater among the elderly, females and hospitalized clients.
Differet types of hyponatremia develop depending on the cause and pathophysiological mechanisms.
Classification of hyponatremia, according to onset, includes acute and chronic hyponatremia.
Acute hyponatremia often involves a rapid reduction in the sodium concentration, which may potentially lead to coma because of a very fast physiologic change.
Chronic hyponatremia on the other hand involves a gradual reduction in the serum sodium concentration making the signs and symptoms less noticeable. Some patients may even be asymptomatic until they reach a significant reduction in the electrolyte level.
Hyponatremia Types
Hyponatremia are classified into the following types depending on the osmolality (concentration) of the plasma:
Hypovolemic Hyponatremia
Hypovolemic hyponatremia involves a low serum concentration of sodium together with low circulating blood volume. It involves the abnormal excretion of both sodium and water leading to low circulating blood volume and serum sodium concentrations. This type of hyponatremia also involves the faulty osmosis of sodium to other extracellular compartments, such as the interstitial space, leading to a decrease in sodium blood levels and subsequent water depletion. In hypovolemic hyponatremia, sodium loss is greater than water loss.
Euvolemic or isovolemic Hyponatremia
Euvolemic or isovolemic hyponatremia occurs when there is a reduction in sodium concentration as a result of excessive production of antidiuretic hormone as seen in Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) or as a result of stress and medication use. Antidiuretic hormone inhibits the kidneys to eliminate water through urine formation. A very high level of ADH inhibits water excretion. As a result, blood volume increases thereby diluting the serum concentration of sodium, leading to hyponatremia.
Hypervolemic Hyponatremia
Hypervolemic hyponatremia results from excessive total blood volume as a result of edema. Because of edema formation, there is a reduction in circulating blood volume, which stimulates the body to produce ADH. Cascade processes happen such that an increase in ADH leads to water retention and subsequent sodium reduction.
Another classification of hyponatremia includes redistributive hyponatremia. This happens in cases of hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia is an increase in immunoglobulin levels or hyperlipidemia wherein there is fluid shifting from the intracellular to the extracellular space. This shift of fluids dilutes the sodium concentration in the blood or plasma.
Hyponatremia Levels
Hyponatremia can also be categorized based on the level of serum sodium such as:
Mild Hyponatremia
Mild cases of hyponatremia involves a serum sodium level of 130 to 134 mEq/L. Mild cases may involve mild symptoms of the condition and may be treated with dietary increase in sodium or oral supplements.
Moderate Hyponatremia
The serum concentration of sodium is from 125to 129 mEq/L. Moderate hyponatremia requires intravenous administration of sodium to prevent further drop in the serum concentration.
Severe Hyponatremia
Severe cases of electrolyte imbalance happens when the serum sodium level is less than 125 mEq/L. Patients with severe cases of hyponatremia have higher mortality rates due to heart blocks as a result of the decrease in excitability of the heart. Neurologic symptoms are often observed. Patients with severe hyponatremia need emergency measures to treat the electrolyte imbalance.
Pathophysiology of Hyponatremia
As the extracellular fluid concentration of sodium decreases, the sodium concentration gradient between extracellular and intracellular fluid decreases. This hypo-osmolality leads to intracellular edema because fluid shifts from low sodium concentration to high sodium concentration. As in this case, the intracellular compartment has a higher sodium concentration so water tends to shift there. Brain edema may occur as a result of shifting of fluids on the interstitial space, leading to coma.
A reduction in the serum concentration also means that there is less sodium to move across the excitable membranes, which results in delayed membrane depolarization and nerve impulse transmission.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes of hyponatremia depend on the classification of the imbalance. Common causes based on the classification discussed earlier are:
- Hypovolemic Hyponatremia
- Diuretic use
- Diabetic glycosuria
- Aldosterone deficiency
- Prolonged vomiting
- Severe diarrhea
- Renal disease
- Diaphoresis
- Burns
Other causes of hypovolemia
- Euvolemic or Isovolemic Hyponatremia
- SIADH
- Severe pain which stimulates ADH production
- Trauma or other forms of stress
- Hypervolemic hyponatremia
- Congestive heart failure
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Liver cirrhosis with ascites
- Renal failure
- Anasarca or generalized edema
Other causes of hyponatremia include:
- Polydipsia (where the individual drinks up to 12 liters of water a day)
- Over hydration from intravenous fluids
- Hypothyroidism
- Multiple myeloma (due to increase in immunoglobulins)
- Hyperlipidemia
- Hyperglycemia
- Adrenal Insufficiency
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of hyponatremia are related to the low sodium levels to perform its functions. Signs and symptoms include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Lethargy, confusion, or coma
- Headache
- Anorexia
- Fatigue, muscle weakness
- Irritability
- Restlessness
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Seizures
Diagnosis
The primary diagnostic test done to determine hyponatremia is through electrolyte testing of sodium. A serum sodium concentration of less than 135 mEq/L confirms the diagnosis.
Vital signs, especially blood pressure and hemodynamic status, needs to be assessed to determine any volume depletion or overload. It is important to ascertain the type of hyponatremia to guide treatment choices.
The patient is also assessed for a complete medical history to determine any underlying cause. Neurologic testing is also done to assess extent of signs and symptoms.
Management (Treatment guidelines)
Management of hyponatremia also depends on the classification.
Determination and management of the underlying cause is essential to permanently correct hyponatremia.
Fluid replacement
Intravenous fluid administration is done for hypovolemic hyponatremia. Normal saline solution is usually used to prevent sudden elevation in the sodium levels, which is also detrimental for the patient. Sodium replacement should be at a rate of 8 mmol/L in 24 hours.
Fluid restriction
Restricting fluids is important for euvolemic and hypervolemic hyponatremia to prevent further increase in the circulating blood volume which will result in edema formation. Fluid restriction also allows sodium balance to be regained.
Vasopressin Receptor Antagonist
These are drugs that inhibit the action of vasopressin by blocking the receptor sites. These drugs are important to prevent further increase in blood volume as a result of its antidiuretic effect. Vasopressin antagonists are used in hypervolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia.
Vaptan drugs are newer forms of vasopressin receptor antagonists that specifically antagonize certain receptor sites such as V1A, V1B and V2 receptors. Examples of this drug are Conivaptan, Nelivaptan, Relcovaptan, Lixivapotan, Mozavaptan, Satavaptan, and Tolvaptan.
Diuretics
Loop diuretics are used to enhance water secretion in hypervolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia. Hypokalemia should be checked since loop diuretics also excrete potassium in the urine.
Source – crashingpatient.com
Complications
Complications include effects of low sodium levels to the vital organs of the body such as:
- Neurologic impairment
- Cerebral edema and herniation
- Coma
- Cardiac arrest
Rapid administration of sodium may also lead to central pontine myelinolysis (CPM), the demyelination of the pons.
Hyponatremia Prevention
Hyponatremia can be prevented using the following measures:
- Drink fluids during extensive exercises to replace fluid loss. Also, try consuming fluids with minimal amount of electrolytes, such as sports drinks, to replace sodium lost through perspiration. Drinking fluids is essential, but taking large volumes, such as more than four liters a day, may also affect the general well-being.
- Consult medical providers to treat any conditions that may lead to hyponatremia.