Sore Tongue – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Remedies
The tongue is one of the most important organs in the mouth that helps us taste, swallow, and speak.
The tongue is composed primarily with muscles. Several factors such as viral infection, trauma, inflammation, and malignancy cause the tongue to be sore, which greatly affects the way we eat and speak.
What is Sore Tongue?
Sore tongue is also called glossitis or Inflammation of the tongue. The sores that appear on the tongue are called glossodynia.
The anatomical position of the tongue makes it prone to infection and inflammation. Any trauma from the surrounding tissues such as the teeth may cause soreness. In addition, the mouth is inhabited by millions of microorganisms and any reduction in immunity may lead to tongue infection.
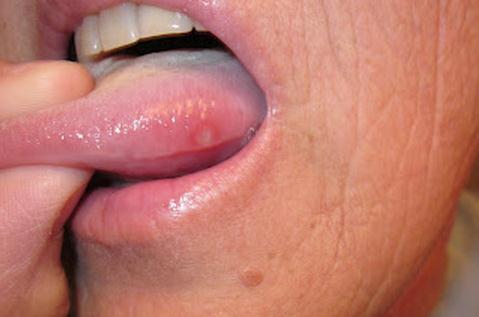
Sore under tongue
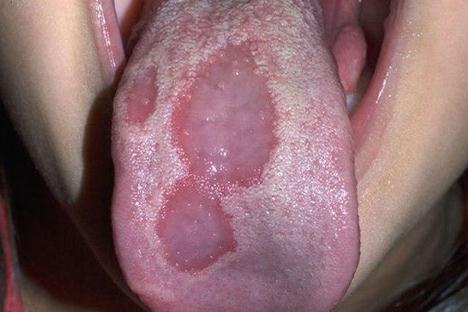
Tongue sores may be located under the tongue. Soreness on the dorsal portion of the tongue may be caused by migratory glossitis or geographic tongue. It affects the dorsal and lateral aspects of the tongue. Sores located in this area may be painful because of contact with the base of the mouth.
Sore on side of tongue
Sometimes, ulcerations or inflammation of the tongue may occur on the sides. This may be caused by herpetic lesions and other mouth infections.
Sore on tongue
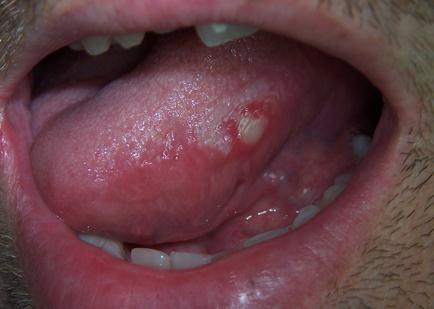
Sores can also be found directly on top which may be present in cases of vitamin deficiencies which changes the texture and color of the anterior portion of the tongue. Fungal infection also thrives on top of the tongue which leaves a whitish discoloration signifying the growth of the fungi.
Canker Sore tongue
A canker sore or apthous ulcer may be present on the tongue. These are open tongue lesions or sores that appear whitish in color that may feel like a burning sensation in the mouth. Canker sores may be three to 10 mm in size. A lot of factors cause the appearance of canker sores including diet, infection, nutritional state and trauma.
Malignant Sore on tongue
Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity causes extensive vascular and lymphatic spread of mouth sores. It causes sores throughout the oral cavity including the tongue. It is caused by tobacco overuse.
Causes
Any change in the environment of the mouth can cause glossitis. Causes of tongue sores can be subdivided into the following:
Habits
Smoking, chewing tobacco and alcohol intake disrupts the moisture and irritates the mucosal lining of the tongue leading to glossitis.
Infection
Fungal infection is one of the main infections of the tongue that leads to inflammation. Candida albicans fungi cause oral thrush that leaves a whitish discoloration of the tongue.
Bacterial growth such as streptococcus bacteria also causes scarlet fever that leaves the tongue sore and strawberry-red in color. The disease is most common in young children.
Viral infections caused by herpes simplex also cause tongue sores. It is transmitted through direct contact with the person’s saliva or fluid such as kissing and licking. Oral herpes can also be transmitted through oral sex with a person with genital herpes.
Medications
Excessive use or abuse of antibiotics destroys the normal flora in the mouth that protects it from infection. Antibiotics not only kill pathologic bacteria, but also the good bacteria in the body. Once destroyed, other opportunistic infections from fungi, bacteria and virus may set in causing tongue sores.
Administration of ganglion blockers and bronchodilators has also been a reason for glossitis.
Trauma
Brushing with toothbrush with hard bristles may also lead to irritation and inflammation of the tongue. Aside from this, scraping too hard on the surface of the tongue also damages the mucosal lining.
Irritation from the adjacent teeth and dental appliances also leads to inflammation of the tongue area.
Tongue piercing causes frequent irritation of the tongue by the ornament. Infections such as Candidiasis may also affect the tongue piercing.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Certain anemia causes sore tongue. Megaloblastic anemia, caused by folic acid deficiency and pernicious anemia caused by Vitamin B12 deficiency leads to a smooth, beefy tongue. In addition, iron deficiency anemia also causes sore mouth and tongue and turns the color into yellow as a result of decreased hemoglobin.
Diet
Excessive consumption of sugar and sweets allows bacteria to grow and cause infection. Intake of acidic foods, juices and spices also irritates the tongue. Frequent chewing of gums and intake of fats and butter may also lead to tongue sores.
Illness states
Certain diseases manifest glossitis. These include tuberculosis, dehydration, and oral malignancies.
Sensitivity reactions
Sensitivity to certain foods and drugs lead to allergic reactions in the oral cavity that causes sore tongue. Allergic reactions may also happen in certain toothpastes, mouthwash, and dental appliances such as retainers.
Symptoms
Patients may experience several symptoms of sore tongue depending on the causative factor. Most common symptoms of sore tongue include the following:
- Tingling or burning sensation in the tongue
- Tongue swelling and pain
- Open sores
- Redness around the tongue sores
- Lymph node swelling as a sign of infection
- Pain in the teeth
- Fever
- Tongue discoloration (depending on the cause)
- Unusual texture (may be smooth or very rough)
- Difficulty chewing and swallowing
- Changes in tastes, loss of appetite
Treatment
Complete eradication of sore tongue is primarily focused on the treatment of the causative factor. Palliative managements for glossitis include:
Anti-inflammatory medications
Administration of analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications is needed to reduce the pain and inflammation in the area.
Local anesthetics
Anesthetics may be prescribed to control the pain in cases of very painful ulcers and sores.
Antibiotics, Anti-fungal and Oral antiseptics
Glossitis caused by infections need to be treated with medications to kill the microorganisms. Oral antibiotics as well as antiseptic washes may be used to reduce the duration of ulcers.
Vitamin B Complex Supplements
The administration of B vitamins helps in the prevention of tongue sores as a result of Vitamin B deficiency. B vitamins are also essential in treating recurrent ulcers and sores not caused by vitamin B deficiency.
Remedies
Home remedies are also effective in managing sore tongue. These include:
- Gargle with lukewarm water with salt to relieve pain.
- Gargle with diluted antiseptic mouthwash to reduce bacterial colonization. Avoid alcoholic mouthwashes because it further leads to drying and irritation of the mouth.
- Drink warm milk mixed with ½ teaspoon of turmeric powder. Turmeric has been found to hasten healing of sores.
- Drink plenty of water to provide the tongue with adequate moisture.
- Try ayurvedic remedies such as Khadiradi tablets and Triphalachuma mouth rinse.
Prevention
- Practice good oral hygiene to prevent mouth infections.
- Avoid chewing gum because it increases tongue sores and exacerbates symptoms.
- Avoid smoking, alcoholic beverages and tobacco.
- Avoid irritating and spicy foods.
- Avoid unsafe sex practices such as oral sex.
- Refrain from using toothpastes with sodium lauryl sulfate. This compound increases the risk for sore tongue and mouth ulcers.
- Use soft-bristled toothbrushes to avoid trauma.
Complications
Complications of sore tongue are associated with the underlying cause. Failure to seek medical treatment can result in further complications such as:
- Difficulty breathing due to airway obstruction
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing
- Chronic pain
- Spread of infection to other parts of the oral cavity
- Malignancy that may lead to removal of the tongue
We do not want these complications so it’s better to seek treatment at an early stage.
Sore Tongue Pictures