PostHerpetic Neuralgia – Treatment, Symptoms, Causes, Prevention
What is Post-Herpetic Neuralgia?
PostHerpetic Neuralgia is a complication of Herpes-Zoster which is defined as a painful condition that normally showsup when the Herpes-Zoster is already in the healing process. Herpes-Zoster is a viral disease, causing painful rashes and accompanied by blisters. Normally, it affects elderly people, aged 50 years old and above.
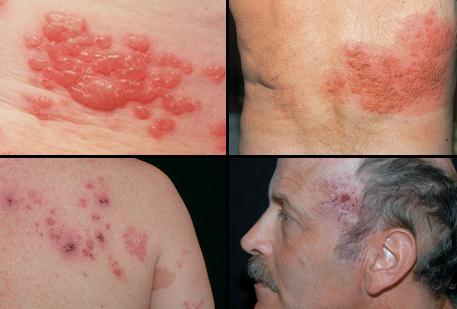
Source – medicinenet.com
PostHerpetic Neuralgia Signs and Symptoms
- Pain for three months or more
- Stabbing or burning pain
- Rashes on the chest, forehead, stomach, or any parts of the body
- Formation of blisters that eventually will heal but pain lingers
- People with PostHerpetic Neuralgia are sensitive to touch because of the sensitivity of the nerves
- People who have this disease are also sensitive to temperature changes.
- Feeling of numbness if the nerves involved control the movement of an individual
- Itchiness and headaches
Causes
PostHerpetic Neuralgia is caused by Varicella Virus which is also is the virus present in the chicken pox, but the difference is that chicken pox is normally seen in children while PostHerpetic Neuralgia is seen in older adults. When a person has had chicken pox, some of the virus remains in the nerve cells of the body. Years later when the person’s immune system decreases, it can possibly reactivate the virus and lead to the formation of Herpes-Zoster. This disease usually occurs when the nerve fibers in our body become damaged during an occurrence of Herpes-Zoster. This disease is due to changes in the nervous system caused by complications of Herpes-Zoster. Since this disease is caused by the development of the Variccela Virus reactivated during the healing stage of Herpes-Zoster, the damaged fibers have difficulty sending messages from the skin to the brain that causes the “pain” message to be disorientated and overstated, resulting in burning, piercing pain that the person will experience for months.
Pathophysiology
- Stage 1 of Varicella Infection: chicken pox during childhood
- Stage 2 of Varicella Infection: latency period or where the Varicella Virus is in state of inactivity
- Stage 3 of Varicella Infection: reactivation of Varicella Virus: Herpes-Zoster – in older adults as their immune system decreases
- Stage 4 of Varicella Infection: PostHerpetic Neuralgia – during the healing stage of Herpes-Zoster Infection
PostHerpetic Neuralgia Treatment
Treatment for this disease will depend on the pain the person experiences and patient’s physical and neurologic health. These treatments are:
Non-Pharmacological Treatment
- Use of loose-fitting clothing to reduce the irritation caused by the disease.
- Pain may eased by cooling the affected area like ice cubes wrapped in a cloth or plastic or by giving the patient a cool bath.
- Relaxation Techniques are used to distract the mind from the pain. It helps the person to relax, to reduce levels of anxiety and stress as a result of the pain.
- Heat therapy as a rehabilitation purpose that can decrease pain, reducing the inflammation and increase blood flow that will provide better healing.
- Nerve stimulation is a type of treatment using a small amount of electricity to stimulate the nerves for healing purposes. It is normally recommended by medical professionals to treat pain.
- Spinal Cord Stimulator is a device used on patients to send electrical signals in the spinal cord to help to control the pain.
Pharmacologic Treatment
- Analgesics is known to relieve pain. Some analgesic used are aspirin, lidocaine patches and paracetamol.
- Antidepressants is helpful to cure both depression and pain. This type of medication is given to patients in a low-dosage compared to patients with depression. Most of the anti-depressant drugs don’t eliminate pain, but they make the pain tolerable.
- Anticonvulsant medication is used for patients to treat muscle spasms and help in pain modulation. .
Prevention
The best method to prevent the disease is to have early treatment when Herpes-Zoster appears. Contact a medical professional once there are signs of Herpes-Zoster to reduce your chance of having the disease. The best way to prevent PostHerpetic Neuralgia is vaccination against chicken pox as well as Herpes-Zoster.
- Chicken pox vaccine is given to the children between the age of one year and one year four months, but it can also be given to adults who have never experienced chicken pox. This type of vaccine doesn’t means that it can provide 100% protection against the disease, but it can lessen the possible risk of complication and it can reduce the severity of the disease.
- Herpes-Zoster vaccine can help older people who have already experienced chicken pox. Like the chicken pox vaccine, it doesn’t guarantee 100% protection against the virus. It can lessen the possible risk of complication and help in reducing the severity of the disease. The vaccine is used only for protection, not for treating people who are already infected. People aged 60 and above are advised to have this vaccine to prevent complications due to a decreased immune system that might reactivate the Varicella Virus and eventually lead to Post-Herpatic Neuralgia