Wheat Allergy – Symptoms, Diet, Test, Rash, Treatment
What is Wheat Allergy?
Wheat allergy is a type of food allergy as a result of ingestion or contact with the different components of wheat. Wheat allergies involve the response of the mast cells and IgE which produces allergy symptoms. Allergies to wheat are commonly due to exposure to the seed storage proteins found in wheat; however, patients may also be allergic to various seeds and plants. There are a total of 27 allergens associated with wheat allergy.
Wheat allergy may be confused with celiac disease and gluten intolerance. The former involves an allergic reaction to proteins in wheat while the latter two cause problems in the intestines as a result of exposure to gluten, a specific protein in wheat.
Symptoms and Signs of Wheat Allergy
Symptoms of wheat allergy are general to all people; however, there are certain symptoms specific to women, adults and children. General symptoms include:
- Hives
Hives, or urticaria, are raised, bordered, reddish skin patches that are often itchy. They may occur singly or in multiples as a wide reddish patch on the skin. Urticaria is a sign of anaphylaxis and may indicate a life-threatening reaction.
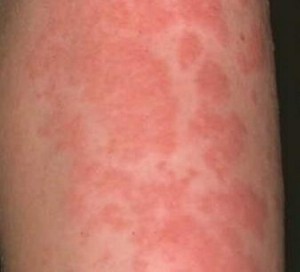
Hives
- Angioedema
Angioedema is the presence of swelling of the tissues as a result of increased permeability of blood vessels leading to movement of blood from the intravascular space into the interstitial space. Angioedema is mostly observed in the face and leads to swelling of the lips and other tissues.
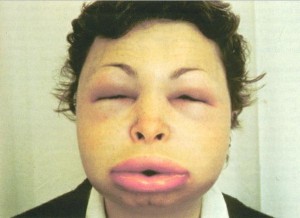
Angioedema
- Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, or hay fever, is the presence of a runny nose along with itchiness and irritation of the nasal passage.
- Nausea and vomiting
This symptom is a reaction of the body attempting to remove the wheat from the digestive system or inside the body.
- Abdominal cramps
Allergies to wheat also causes the intestinal mucosa to become irritated, resulting in smooth muscle spasms and causing abdominal cramping.
- Diarrhea
Diarrhea may also be experienced due to the mechanism of the body to eliminate all foreign substances.
- Tiredness and lethargy
Allergic reactions to wheat also increase the body’s rate of functioning in order to fight the foreign substance, thereby leading to lack of energy.
Symptoms in women
- Mood swings
Women may experience changes in mood due to an affectation of the nerve impulse transmission.
- Hypogastric pain or dysmenorrhea
The presence of swelling of the sacroilial joint may be present as dysmenorrhea when the allergic reaction occurs during menses.
Symptoms in adults
- Sacroilitis
Sacroilits is the inflammation of the sacroilial joint. Wheat allergies cause the area to swell and inflame as a result of inflammatory response.
- Eczema
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is the occurrence of rashes on the skin as a result of histamine release by the mast cells, causing vasodilatation and development of scaly rash on the skin. Eczema is often itchy and causes severe dryness of the skin. Eczema can occur in all parts of the body such as the face, arms, back and trunk.
- Palpitations and chest pain
Adults may experience heart irregularities, especially when there is an anaphylactic reaction or severe allergy. This results from increased heart contractility, resulting in conscious feelings of heart contractions.
- Joint and muscle pains
Arthritis may also be experienced because of circulation of antibodies to the joints which may lead to damage.
Symptoms in children
- Unexplained cough and asthma
Children often exhibit asthma attacks and an unexplained cough. Asthma is more apparent when the child is really asthmatic. Baker’s asthma is a specific allergic reaction to uncooked wheat flour.
- Swelling of the tongue and throat
There is also pharyngitis that is easily seen in children who suffer from allergic reactions.
- Wheat allergy rash
Children often do not develop severe eczema. A maculopapular rash may be more apparent in children.
Causes of Wheat Allergy
The main cause of wheat allergy is exposure to different proteins in wheat as a result of ingestion, inhalation or skin contact with these substances. Generally, the main cause is ingestion through food. Foods that contain wheat proteins include:
- Breads
- Pastries
- Cereals
- Couscous
- Pasta
- Spelt
- Farina
- Semolina
- Beer
- Crackers
- Soy sauce
- Vegetable protein
- Ketchup
- Hot dogs
- Ice cream
- Starch
- Vegetable gum
- Jelly beans and candies
- Licorice
People who are allergic to wheat may also have similar reactions to barley, rye and oats.
Wheat Allergy Testing
Diagnosis of wheat allergy begins with a medical history that might indicate family history of allergies as well as symptomatology. A food diary may also be required to determine the foods that have been taken in. Further testing includes:
-
Skin test
A solution containing small amounts of wheat proteins are injected under the skin to determine if there is an allergy to wheat. The small amount of wheat helps to identify allergy even from the smallest proportion.
-
Antibody testing
Testing for IgE antibodies may also be done to determine presence of immunologic markers for wheat allergy.
-
Food challenge testing
This test involves the ingestion of capsules containing possible allergens. The presence of symptoms following ingestion within hours to days may indicate allergy.
Treatment of Wheat Allergy
The single, most effective way to manage wheat allergy is through avoiding exposure to wheat proteins such as eliminating them from the diet. However, some patients may still ingest portions of wheat in products. With this, specific treatments include:
Medications
Medications such as anti-histamines reduce the symptoms of allergy by binding the histamine receptors to prevent symptoms. Anti-histamines include diphenhydramine, cetirizine, and others. These medications may cause sedation so safety should always be ensured. In cases of anaphylaxis, epinephrine is given to provide emergency management for severe reactions. Epinephrine is usually injected intramuscularly. Patients with allergies are advised to carry epinephrine injections all the time for emergency purposes.
Diet and Recipes
Aside from medications, avoiding the allergen means dietary modifications and restrictions. Wheat products should be avoided. However, lack of wheat intake may also yield deficiencies in fiber. Because of this, wheat-free oats can be used to supply the body with the needed dietary fiber. Recipes that contain wheat-free goodies are also available online. They are easy to prepare and as tasty as foods containing wheat.