Underactive Thyroid Symptoms, Treatment, Diet in Women and Men
What is Underactive Thyroid?
Underactive thyroid or medically known as hypothyroidism is a condition wherein the thyroid glands do not produce enough thyroid hormones for the body’s use. Thyroid hormones such as triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) are essential in the regulation of the body’s metabolism. Limited amounts of thyroid hormones lead to slowing down of the metabolism and body processes.
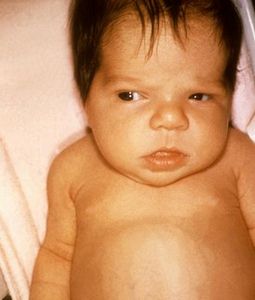
infant with Underactive Thyroid Symptoms
Source – clivir.com
Underactive Thyroid Symptoms and Signs
Hypothyroidism causes symptoms that are a result of the slowing down of body processes; hence there is affectation of all body processes. Hypothyroidism symptoms appear gradually and some patients may not even notice its occurrence. This condition is known as subclinical hypothyroidism. Most of the symptoms of underactive thyroid include:
Common Symptoms
- Cold sensitivity – The slow metabolism leads to poor heat production and causes the patient to feel cold easily.
- Fatigue and drowsiness -Slowing of body processes also makes the person sleepy most of the time with feelings of fatigue because of low energy production.
- Drying of the skin – Drying of the skin may be related to decrease in sweating hence, lack of skin moisture is experienced.
- Paleness – Patients may also have delayed formation of red blood cells leading to anemia. Anemia shows as paleness and weakness.
- Brittle hair and nails, thinning of hair – The formation of a strong matrix in the hair and nails is also impaired because of slowed body metabolism.
- Change in facial expression – Facial expression is also affected because of affectation of the face such as the appearance of moon face due to water retention.
- Slowed movements, sore muscles and weakness – Decreased metabolic rate means decreased energy production. As a result, the patient may have weakness and slowing of body movements.
- Constipation – The digestive system is also affected leading to slowing of the peristaltic activity. This further leads to constipation.
- Weight gain – Poor metabolism allows the body to store food rather than utilizing it for energy production. The patient experiences severe weight gaining over a short period. Weight gaining may also be caused by water retention because of the decreased formation of urine by the kidneys.
- Bradycardia – Low thyroid hormones do not stimulate the contraction of the heart leading to slowed heart rate. Bradycardia is more evident at night when the body is at rest. Patients should be monitored for heart failures.
- Elevated cholesterol levels – Lipids are also not metabolized and used by the body thereby there is elevation of cholesterol levels.
Late symptoms
- Goiter or the enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Hoarse voice due to goiter
- Decreased basal body temperature
- Depression
Other symptoms related to slowed brain functioning may also arise. These include:
- Impaired memory
- Inattentiveness
- Slow reflexes
Symptoms in women
Certain symptoms may also be specific to women such as:
- Increased risk for abortion or miscarriage – When metabolism is slow, fetal development is also affected due to poor nutrition to the fetus.
- Fertility problems – The ovaries may not be able to produce egg cells regularly because of impaired body functioning.
- Prolonged, heavy and irregular menstrual period – Thyroid hormones are responsible in regulating the menstruation. Absence or lack of hormones may lead to heavy menstruation.
- Galactorrhea – Similar to the mechanism in menstruation, there is increased production of prolactin that stimulates the cells to produce milk despite being not pregnant or not nursing a baby.
Symptoms in men
Symptoms in men may include:
- Fertility problems – The testosterone levels in the body are also reduced leading to difficulties in spermatogenesis.
- Decreased libido – The affectation of the testosterone also reduces the sexual functioning in men.
- Gynecomastia – Gynecomastia is the development of enlarged breast tissue in men as a result of increased estrogen levels.
Causes of Underactive thyroid
Specific causes of underactive thyroid are related to the destruction of the thyroid gland as well as problems on the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, which regulates thyroid function. These include:
- Hashimoto thyroiditis – This is an autoimmune disease that leads to the destruction of the thyroid gland by the body’s own immune cells.
- Congenital anomalies – Women exposed to teratogens may have baby with congenital hypothyroidism that will be present indefinitely.
- Pituitary tumors – The presence of problems in the pituitary gland leads to a reduction in the thyroid stimulating hormone, which stimulates the thyroid glands to produce T3 and T4.
- Iodine deficiency – Lack of iodine in the diet predisposes to decreased production of thyroid hormones because iodine is the basic component of thyroid hormones.
Treatments for hyperthyroidism – Medications and surgery to treat overactive thyroid may accidentally reduce its functioning thereby leading to underactive thyroid.
Medications – Medications such as amiodarone (anti-arrhythmic) and lithium carbonate (anti-manic drug) may also affect the thyroid glands and cause decreased production of hormones.
Diagnosis of Underactive Thyroid
Diagnosis of underactive thyroid is done by assessing the TSH and thyroid hormone levels. A high level of TSH with low T4 may indicate underactive thyroid that originates from the thyroid itself. A low level of TSH together with T4 signifies problems on the pituitary gland or hypothalamus. Circulating antibodies may also be assessed to determine autoimmune diseases.
Treatment
Treatment of hypothyroidism is based on medical approaches. Surgery is not a treatment of choice because it cannot reverse the damage to the thyroid gland. Medical therapy involves:
Synthetic Thyroid Hormone Administration – Synthetic hormones are usually given to supply the body with thyroid hormones that are needed to undergo normal metabolism. An example of this drug is Synthroid or levothyroxine. These medications can improve symptoms and may reverse cold sensitivity, weight gaining, weakness, fatigue, dry skin and hair loss. Thyroid hormones are administered daily 30 minutes to one hour before breakfast to maximize absorption. Calcium and caffeine should be avoided because these inhibit the absorption of thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormone levels are also monitored to prevent sudden increase and too much thyroid hormone that may lead to overactive thyroid.
Thyroid replacement therapy may take one of these combinations:
1. T3 and T4 combination
2. Levothyroxine only
3. Desiccated Thyroid extract (an animal-based thyroid extract, which comes from porcine sources).
Thyroid replacement therapy is usually increased pregnancy.
Diet and Natural Remedies
Some patients with hypothyroidism may not require medications and can be managed with proper diet and home remedies. Before taking any home remedies, it is best to consult a physician.
Diet
Diet is an important factor for the prevention and treatment of hypothyroidism. An increase in goitrogens or foods that cause low levels of thyroid hormone plays as role in the development of underactive thyroid. These foods include cauliflower, cabbage, radish, broccoli, soy, millet, kale, and Brussels sprouts. Management of hypothyroidism includes avoiding these foods and substituting it for iodine rich foods such as sea foods and the use of iodized salt.
Other home remedies include:
- Increase selenium intake – Selenium is very important in the management of underactive thyroid. Selenium serves as a stimulant in the conversion of T4 to T3. Selenium can be found in salmon, snapper, halibut, tuna, cod, shrimp, and mushrooms.
- Consume tyrosine rich foods – Tyrosine is responsible for manufacturing thyroid hormones from iodine. It is found in lean meat, fish, wheat, dairy products and oats.
- Consider using herbs – Herbs such as ginseng, black cohosh and spirulina are beneficial for people with underactive thyroid.
- Consume small frequent meals – Instead of taking three big meals, substitute it with six small meals because small meals with good quality improves metabolism.
- Engage in exercise – Exercise allows the body to hasten metabolism and also helps people with hypothyroidism to lose weight and increase immunity.
Underactive Thyroid Problems and Side effects
Complications of hypothyroidism include those that results from slowed body metabolism such as cardiomyopathy, heart failure and myxedema coma. Myxedema coma is a life-threatening condition arising from underactive thyroid.