Ectodermal Dysplasia (Hypohidrotic) – Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment
What is Ectodermal Dysplasia?
Ectodermal Dysplasia is a group of disorders that is congenital and inherited. It affects the tissues of the ectoderm, the outermost layer of the Embryo. A person with Ectodermal Dysplasia has deficiency in the following structures: hair, nails, teeth, and sweat glands. The Ectoderm is involved in developing the nervous system, teeth, epidermis, mucosa, sweat glands, hair and nails.
The first clinical incidence with the same features of Ectodermal dysplasia was during 1792; two Jewish boys had no hair and teeth at birth. At present, there are approximately seven cases per 10,000 affected with Ectodermal dysplasia worldwide. In the United States, there are estimated cases per 10,000. HED is more common among Caucasians, but there cases come from other races as well.
Types
a. Hypohydrotic
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (also known as Anhidriotic ectodermal dysplasia) is the most common type of Ectodermal dysplasia characterized by deficiency in the following:
- Hair
- Teeth
- Sweat glands
- Mucosa.
There are three inherited types of HED:
- X-linked recessive HED – the most common type of HED
and the two uncommon type are:
- Autosomal dominant HED
- Autosomal recessive HED.
The incidence of HED is approximately 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 100,000 male live births.
Symptoms
- General symptoms include:
- Height that is below expected
- Repeated acute infectious diseases
- Fever with unknown reason that occur mostly among infants
- Hoarseness of voice
Clinical symptoms:
- Hypodontia (missing teeth)
There is a problem in the development of the teeth resulting in an incomplete number of teeth. Teeth that appear are smaller than the normal size and with cone shaped crowns.
- Anhidrosis or lack of sweating
Due to malfunctioning of the sweat glands, the body cannot properly control the temperature, thus leading to Hyperthermia or an increase in temperature
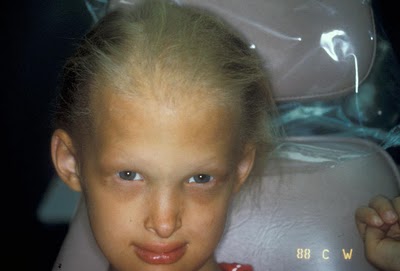
- Hypotrichosis or abnormal hair growth
Growth of body hair is scattered, thin, light in pigment, slow growing, and fragile.
- Skin
Infections, cracking and bleeding of the skin are common. Unusual pigmentation of the skin is also observed. It can be light pigment, but in some incidence, red or brown pigment occurs.
- Nails
Abnormalities in the shape of the nails and it affects both the fingernails and toenails. Different color of the nail, slow growing and brittleness are also present.
- Broader nose
Hollow nasal bridge
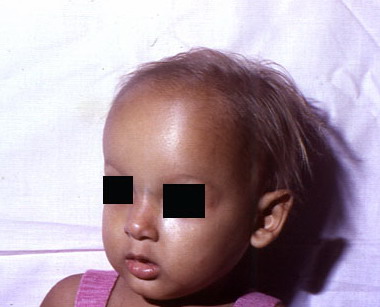
- Frontal bossing
Abnormal, noticeable forehead.
Frontal bossing in Ectodermal Dysplasia
- Vision defects
Usually leads to eye infection, cataracts and other eye disorders.
Causes
1. Genetics
Patient siblings
- X-linked recessive: if the mother is the carrier, there is a 50% chance to be inherited.
- Autosomal dominant: there is a 50% risk for the siblings to be a carrier; unless the parent is affected, there is no increase of possibilities.
Patients’ offspring
- X linked recessive
Male proband: 50% of their daughters will be affected and might demostrate minimal symptoms. None of the sons will be the carier.
Female proband: both son and daughter have 50% risk of being a carrier.
- Autosomal dominant: each child has a 50% risk.
- Autosomal recessive: there is a 50% risk in the offspring.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic procedures can be done to identify other disorders associated with Ectodermal Dysplasia.
Radiography
Radiographic procedures like Xrays of the extremities can show defect in the bones. Visualization of the kidney through Ultrasound or Intravenous pyelography can assess if the patient is developing anomalies in the urinary system.
Hystopathology
Skin biopsies can identify if there are decrease or absence of sweat and eccrine glands.
Genetic mutation analysis
It is a Prenatal Diagnosis for pregnants carrier of Ectodermal Dysplasia.
Analysis of the Chronic Villi
Treatment
There is no specific treatment to cure Ectodermal dysplasia, but there are many ways to diminish the symptoms.
Temperature
- Provide a cooling environment inside and outside home with the use of air conditioning, fans and proper ventilation.
- Drink enough water, especially during the hot season.
- Wear clothes made of cotton.
Dental management
- Visit your dentist regularly to monitor the conditions your teeth
- Wear dentures
- Dental implantation
Others
- For dry skin, use moisturizers to prevent eczema and further complications.
- For the eyes, artificial tears through eye drops can be used to prevent corneal damage.
- For nasal congestion, you can remove secretions with the use of suctions and humidification of air.
- Avoid strenuous activities for patients who lack sweat glands (Hypohidrosis).
- Monitor weight and height.
- To prevent recurring infections, Antibiotics are given for prophylaxis.
- Cleft lip or palate repair is done to improve facial appearance and speech.
- Rehabilation therapy can assist patients in the anomalies they have. Physcial therapy can improve hand and foot abnormalities, speech therapy in speaking and feeding.
Complications
Possible complications include:
- Febrile seizure due to high fever.
- Recurrent infections in the upper respiratory tract are common.
- Inflammation of the scalp that will result to erosion because of Alopecia.
- Failure in growth development.