Glandular Fever – Symptoms, Contagious, Treatment
What is Glandular Fever?
Glandular fever or medically known as infectious mononucleosis is a viral infection involving the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It is also known as kissing’s disease because of its oral transmission. It is also known as Filatov’s disease or Pfeiffer’s disease. It is an acute febrile disease that commonly affects children up to young adults. The infection usually affects the oral cavity with symptoms of sore throat, fever, fatigue and enlargement of lymph nodes.
The specific populations that glandular fever affects are those aged 10 to 25 years old. EBV is a type of a herpes virus belonging to the family of Herpesviridae. Once the virus reaches the body, it replicates in the cells in the pharynx and affects the B lymphocytes resulting in enlarged lymphocytes.
Glandular Fever Symptoms and Signs
Children usually do not manifest any symptoms or may only experience flu-like symptoms. Other ages may also not experience any problems, but adolescence and young adults develop glandular fever symptoms. These include:
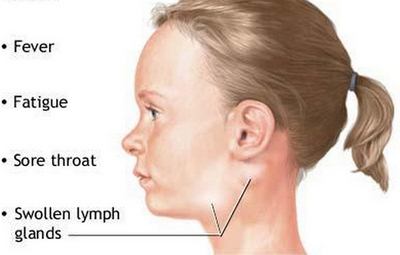
- Sore throat. The Epstein-Barr virus usually stays and replicates on the pharynx, which leads to pharyngitis or sore throat. The throat may be coated with a whitish material. The tonsils are also usually affected.
- Severe fatigue. As with any infection, people suffering from glandular fever may experience severe fatigue as a symptom. This is due to the increased metabolic rate and the loss of energy brought by the virus.
- Fever. Fever is a classical sign of infection. Glandular fever is characterized as having continuous high grade fever.
- Muscle pains. The patient may also experience muscle pains as a result of the virus. This mimics the flu-like symptom of body malaise and myalgia.
- Puffiness around the eyes. The virus may affect the eye area and may cause swelling. This symptom usually resolves rapidly.
- Diaphoresis. Diaphoresis or increased sweating is also experienced by people with glandular fever.
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes. The virus may further spread on the lymph nodes causing it to swell and enlarge. Lymph nodes on the groin, armpit and neck usually enlarge.
- Spleenomegaly. This condition involves the swelling of the spleen because of increased destruction of the B lymphocytes as well as the rapid hemolysis of the red blood cells. The destroyed cells go to the spleen and may cause mild pain on the left upper quadrant below the ribs.
- Enlargement of the liver. The liver may also experience swelling because of circulation of the virus to the area. The affectation of the liver also results in jaundice or the yellowish discoloration of the skin.
- Glandular fever rash. A non-itchy skin rash may also develop in all parts of the body, which eventually disappears.
- Loss of appetite. Patients may also experience loss of appetite as a result of inflammation of the throat.
- Difficulty of breathing. Patients may also experience dyspnea because of obstruction of the upper airways as a result of severe pharyngitis.
Severe symptoms of the disease include rupture of the spleen, low platelet count, low white blood cell and red blood cell count and the presence of erythema multiforme or a severe development of skin rash.
Diagnosis of glandular fever is very important because it mimics other diseases such as streptococcal infections, influenza, diphtheria, leukemia and common colds. Classical symptoms of glandular fever are confirmed by blood tests that identifies problems on the lymphocytes. Heterophile antibodies are also identified.
How do you get Glandular Fever?
Glandular fever is spread through direct contact with the person’s saliva as well as through droplets. It is termed as kissing’s disease because the most common transmission is through kissing an infected person or a contact with the infected oral secretions. Symptoms of glandular fever usually occur 30 to 50 days after the exposure to the virus.
Can you get Glandular Fever twice?
Glandular fever stimulates the formation of active natural immunity once the patient suffered the infection. The body produces antibodies that detect the presence of the virus next time the person gets exposed. Because of this, it is uncommon that a person can have glandular fever twice because of the life-long immunity it develops. However, some patients may experience period of inactivity wherein the person develops a dormant infection. Once the virus becomes active again, the person becomes infectious again, but may not experience symptoms anymore.
Glandular Fever Treatment
Glandular fever is a viral infection, which means that the disease is self-limiting or resolves on its own. There is no specific treatment for the disease and it only requires palliative treatment or symptomatic relief. Managements often involve:
Rest
Rest is an essential management during the acute phase of the disease to relieve weakness and fatigue. Activities are normally resumed after the acute phase. Contact sports and also other high impact activities should be avoided to prevent rupture of the spleen
Medications
Medications are also given to relieve symptoms. Medications include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Medications such as ibuprofen help relieve pain and lower the fever. Aspirin is almost not used especially in children because of potential side-effect of Reye’s syndrome.
- Corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are also used to reduce inflammation in the pharynx and tonsils. The most commonly prescribed steroid is Prednisone.
- Anti-viral medications. Anti-viral drugs such as acyclovir and valacyclovir help reduce viral shedding and it also proven to lessen the Epstein-Barr virus, thereby reducing the severity of the disease. Anti-viral medications are usually given to severe EBV infections and may not be given to mild cases.
- Antibiotic therapy when streptococcal infections arise. In EBV infection with streptococcal infections, antibiotics such as penicillin may be given to treat the bacterial infection. Ampicillin and amoxicillin are contraindicated because of occurrence of non-allergic rash in EBV patients. However, EBV only infections are not prescribed with antibiotics because they are deemed ineffective in eradicating the virus.
- Fluid intake. Increased fluid intake is also beneficial for those suffering fever to prevent dehydration.
- Throat care. Gargling with antiseptic solutions helps in reducing sore throat and pharyngeal infections.
Patients also need to increase the immune system by consuming fruits and vegetables as well as vitamin C supplements to prevent secondary infections and help in faster recovery.
Is Glandular Fever contagious?
Glandular fever is highly contagious during the first six weeks from the time the signs and symptoms appeared. However, some studies have revealed that glandular fever can be transmitted as long as several months with the longest time of up to 18 months even when the signs and symptoms already disappeared.
The virus easily spreads through kissing, inhaling droplets when the patient coughs or sneezes and using eating utensils infected with saliva.