Legionnaires Disease – Symptoms, History, Treatment, Causes, Prevention
What is Legionnella?
Legionnella is common in the natural environment, specifically in natural watercourses, like ponds and rivers. It is a pathogenic gram negative kind of bacterium. This kind of bacterium, includes the causative factor of Legionellosis or Legionnaires disease.
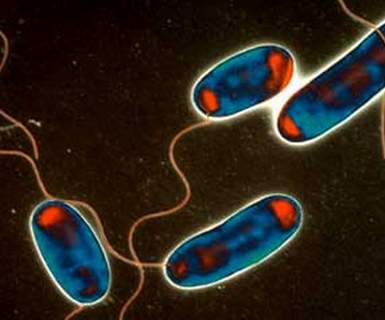
Picture 1 – Legionnella bacteria morphology
What is Legionnaires Disease?
It is a severe kind of lung infection and is fatal if not treated. It is found in natural bodies of water like lakes, rivers, creeks, hot springs, potting mix, warm water systems, spas, and also artificial systems used for heating, cooling or industrial process, like cooling towers.
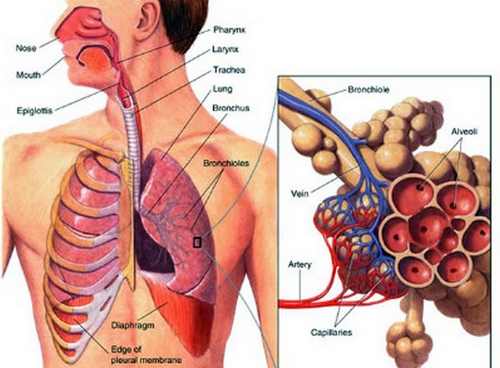
Picture 2 – Legionnaires disease pathophysiology
History
The name originated during the first outbreak of pneumonia among the American Legion convention held in Philadelphia last July 1976. January of the following year, the outbreak agent that caused the disease was identified and was then known as Legionnella.
Symptoms
Persons having Legionnaires disease mimics the same symptoms as persons who have pneumonia, making it hard to diagnose. A person with this kind of disease condition may manifest the following symptoms:
- Chills
- High fever
- Non- productive or productive cough (first sign) with yellowish green sputum or with blood
- Muscle aches
- Headaches
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Stomach discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Confusion
- Lack of coordination or ataxia
- Disorientation
- Hallucination
- Loss of memory
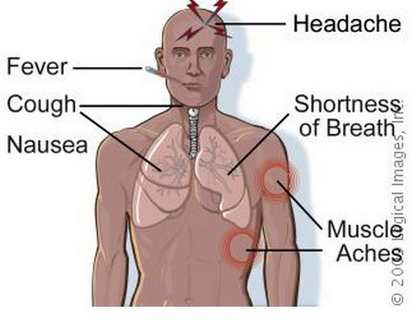
Causes
As mentioned, the causative factor is a bacterium called Legionnella pneumophila, found in the environment, more commonly in water systems.
Diagnosis & Risk Assessment
For patients suffering the above symptoms, a physician will usually perform the following to confirm whether or not it is Legionnaires Disease:
- Thorough assessment
- Physical examination
- Medical history
- Blood test
- Chest x-ray
- Arterial blood gasses
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Liver function tests
- Sputum or bronchoscopic culture
- CT scan of the brain
- Spinal tap or Lumbar Puncture
- Culture test
- Direct fluorescent antibody
- Antibody testing
- Urinary test
People at risk for acquiring this disease are those with:
- Diabetes
- Cancer, most especially persons with leukemia or lung cancer
- Alcoholism
- Chronic kidney disease
- Heart disease
- Chronic lung disease, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- HIV or human immunodeficiency virus or AIDs or commonly known as acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
- Those who are taking immunosuppresant medications as they pose a high threat to the person’s health, specifically his or her immune system.
Treatment
Persons diagnose with Legionnaires disease are likely to be treated with the following:
- Medication, specifically antibiotics – Antibiotics are the number one form of treatment used for this disease. Normally, a physician will prescribe either macrolides or quinolones.
- Fluid and electrolytes replacement – This treatment is done when the patient manifests diarrhea.
- Oxygen Therapy – This treatment is needed when patient have difficulty breathing.
- IV fluids – This treatment is also needed when the patient has been experiencing diarrhea.
- Intensive support systems – This is needed most especially when the patient needs mechanical ventilation.
Complications
When not treated promptly, this kind of disease may lead to more complications such as:
- Kidney failure -At first, the kidneys will perform normally, but over time, as the body can no longer carry out normal activities because everything is affected, the kidneys will shut down. When the person’s kidneys fail, the toxic waste and fluid and electrolytes will accumulate and may lead to death.
- Respiratory failure – What happens in respiratory failure is that the person’ s lungs are no longer able to deliver enough oxygen to the body and also the lungs can no longer remove carbon dioxide, which is not needed by the body, but out of the person’s body.
- Septic shock -Occurs when the person experiences a sudden, severe drop in the blood pressure, leading to blood flow reduction of vital organs, such as brain and kidneys. The body makes the heart compensate for the loss of pressure by allowing it to increase in the volume of blood that it pumps. However, the heart cannot do this for very long without growing tired leading to a reduction of blood flow.
Prevention
With regards to the prevention of having this kind of disease condition, you should remember these important things:
- Hygiene – You must make sure that all the water you use and consume, is clean.
- Temperature – The ideal temperature should not be below 20 degrees Celsius or 68 degrees Fahrenheit and or higher than 60 degrees Celsius or 140 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Good engineering practice – It is also advisable that you practice good engineering in maintaining and operating water and air handling system. You should practice hygienic practices such as cleaning evaporative condensers, cooling towers and the like.
- Travel advisory – If you have any plans to travel abroad or have travelled in an area that has a potential high-risk for getting having Legionnaires disease, you must be well informed about the disease and all of its symptoms and find medical help immediately for further evaluation if you acquire any of the symptoms .
- Avoid smoking – When one smokes, it makes one more vulnerable for acquiring this kind of disease.