Bleeding After Menopause – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
What is Vaginal Bleeding after Menopause?
Bleeding after menopause or post-menopausal vaginal bleeding is the occurrence of vaginal bleeding after the woman has undergo menopausal stage. It may be confusing for women because they are already aware that they have reached menopausal stage and yet, bleeding is still recurring.
Bleeding after menopause also becomes frightening for women because they may feel that something is wrong inside their uterus. Although some bleeding after menopause may be normal because of menopausal therapies, some may be due to more serious problems that is crucial to be noted.
Bleeding menopause has characteristic points such as:
- There is already cessation of menstruation for more than a year before the post menopausal bleeding occurred.
- Post menopausal bleeding may be experienced by up to 30% of menopausal women.
- Bleeding after menopause can be light flow or heavy flow depending on the cause.
- Post menopausal bleeding is primarily concerned with hormonal shift.
- Rare cases of post menopausal bleeding are caused by more serious problems in the uterus.
Post menopausal bleeding is highly treatable. The woman should seek consult as early as possible in order to detect early any possible underlying conditions in the reproductive tract. It is also important to note the characteristic of the bleeding in order for physicians to have a broader view of the condition.
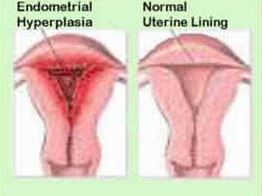
Bleeding after Menopause Image
What Causes Bleeding after Menopause?
Causes of bleeding after menopause are vast, which may involve mild to severe factors. These include:
Hormonal Replacement Therapy – Hormonal replacement therapy is given to regain normal estrogen and progesterone hormonal levels, which reduces the menopausal symptoms. Because of the fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone, post menopausal bleeding may occur.
Poor Vaginal Lubrication – Poor lubrication of the vagina may cause irritation and bleeding during vaginal intercourse. Poor lubrication may also lead to painful intercourse.
Trauma – Trauma from a foreign body or penis may also lead to post menopausal bleeding.
Use of Steroids and Anti-coagulant Therapy – The use of these medications for other conditions may lead to impaired clotting mechanism of the blood thereby leading to possible bleeding after menopause.
Kidney, liver and thyroid diseases that may lead to clotting problems – Kidney, liver and thyroid diseases all contribute to the development of clotting problems because of impaired clotting mechanism of the blood. When these happen during menopausal stage, it may lead to abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Infections – Sexually transmitted diseases such as Chlamydia may also cause vaginal bleeding after menopause.
Endometriosis – Endometriosis is the excessive proliferation of the endometrial lining. This condition usually leads to bleeding even after menopause.
Malnutrition and Stress – These factors also lead to post menopausal bleeding because of altered hormone levels.
Reproductive tract cancers – Cancers of the reproductive tract especially the uterus may lead to abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Anti-cancer drugs – Treatments for cancer also lead to vaginal bleeding. This is especially noted in breast cancer medications because of hormonal content.
Associated Symptoms
Common symptoms of bleeding after menopause include:
- Abdominal, lower back and pelvic pain
- Pain in these areas is commonly due to uterine contraction similar when a person is undergoing menstruation.
- Dyspareunia
- Pain during sexual intercourse may also be experienced because of irritation of the vagina
- Fatigue
- Fatigue is a sign of decreasing levels of hemoglobin as a result of bleeding after menopause.
- Mood swings
- Mood swings may be related to hormonal shifts that occur along with post-menopausal bleeding.
Danger signs of post menopausal bleeding may include:
- Fever and chills
- Fever and chills may be a sign of ongoing infection due to proliferation of bacteria in the blood.
- Tachycardia
- A fast heart rate is an early sign of reduced blood volume or hypovolemia brought by vaginal bleeding.
- Change in bowel movements
- Changes in bowel movements from diarrhea to constipation and vice versa may be a sign of reproductive malignancy that has metastasized to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Unexplained weight loss
- Sudden, unexplained weight loss may also indicate cancer because the cancer cells are consuming most of the nutrients in the body.
Treatment for Bleeding after Menopause
The treatment of vaginal bleeding focuses in ceasing the bleeding to prevent hypovolemia. Treatments also involve symptomatic relief of patients. These include:
Gynecologic Surgery
The primary management of post menopausal vaginal bleeding is surgery. Dilatation and curettage is usually done to scrape the excess uterine lining responsible for post menopausal bleeding. The procedure is done under general anesthesia or by sedation. It involves the use of a curette, a special surgical instrument used to scrape the dysfunctional cells in the uterus.
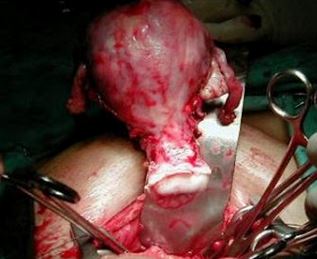
Surgical procedure to treat underlying physiological cause of bleeding after menopause
Image source: menopausebase.com
Anti-fibrinolytic medication
Anti-fibrinolytic medications are given to prevent the destruction of fibrin clots in the body. In this way, the fibrin clots are not dissolved promoting blood clotting. An example of this medication is Tranexamic acid. However, this medication is contraindicated to patients with history of thromboembolism because it may lead to heart attack or stroke.
Platelet transfusion
Platelet transfusion is given to those who have low platelet count. Platelets are responsible for the initial step in blood coagulation.
Other remedies for post menopausal vaginal bleeding include:
- Using pads instead of tampons to prevent irritation of the vaginal mucosa.
- Avoid using aspirin as an antipyretic or anti-inflammatory medication to prevent thinning of the blood.
- Change pads regularly to prevent life-threatening infection or sepsis.
Risks of Bleeding after Menopause
Bleeding after menopause requires immediate consultation to a gynecologist even if some cases remain to be normal as part of menopausal transition. This is because bleeding after menopause can result to various complications especially when the woman experiences heavy vaginal bleeding. Risks include:
Hypovolemia
Hypovolemia is the most common complication of post-menopausal bleeding because of heavy bleeding that depletes the blood volume of patients.
Shock
When bleeding becomes persistent, it may lead to cardiovascular collapse as manifested by severe hypotension.
Sepsis
Sepsis may also result from bleeding after menopause because the blood in the vagina may harbor pathogens. When the infection spreads to the blood, it may lead to sepsis and possible septic shock.
These risks may be life-threatening so early detection and treatment is necessary to prevent severe complications.