Minimal Change Disease – Diet, Treatment, Prognosis, Symptoms
What is Minimal Change Disease?
Minimal Change disease is a condition of the kidney that causes glomerulopathy, there is an impairment happening in the Glomeruli. Glomeruli is a cluster of capillaries that carries blood inside the kidney and filters waste products from the blood and establish formation of urine.
Minimal Change Disease is considered one of the major causes of Nephrotic Syndrome in children, accounting for about 80% among children and accounting 10 to 15% in Adults.
People suffering from other autoimmune disorders are more at risk in developing minimal change disease. Minimal change disease increases the possibility in developing other autoimmune disorders.
Other conditions may also be associated with MCD, most common are Hodgkin disease and solid tumor, interstitial nephritis associated with NSAID (Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) is also included.
Usually, there is a sudden appearance of proteinuria, hypertension, edema of extremities and face and sometimes renal insufficiency.
Alternative names for Minimal Change are the following:
- Minimal change nephrotic syndrome
- Nil Disease
- Lipoid Nephrosis
- Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood
Reports says that Minimal change disease is more common in many industrialized countries like United States, Japan and Spain. Asians have an increased risk. When it comes to gender, boys are more affected than girls.
Symptoms of Minimal Change Disease
-
Proteinuria
The presence of protein to the urine, usually appears suddenly. The urine is foamy in appearance because of excess protein.
-
Edema
Usually starts in the face, next on the abdomen, up to the legs. When the protein is excreted in urine the level of protein in the blood goes down. Causing the Oncotic pressure in the tissue to decrease. The fluid from the vascular compartment will move to the interstitial compartment and will cause fluid retention and swelling in the affected area.
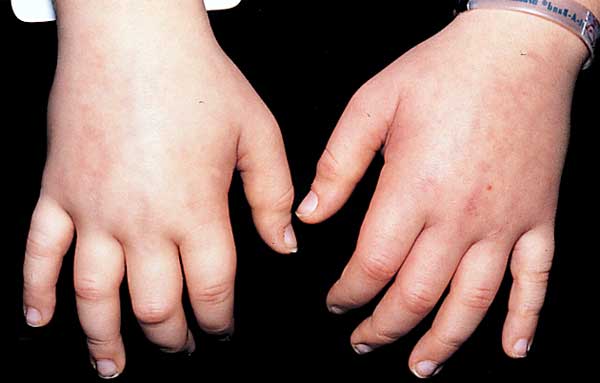
Edema in the hands as a result of decreased oncotic pressure
-
Weight gain
Due to fluid retention
-
Body Malaise and Easy fatigability
A result of extra fluid that retains in the body.
-
Hypovolemia
Early signs of hypovolemia includes abdominal pain and increase in hematocrit.
Causes of Minimal Change Disease
-
Idiopathic
In large number of MCD cases, there is no known etiology and diagnosis is commonly Idiopathic.
-
Neoplasms
Neoplastic processes have been reported most of the time associated with MCD. Conditions like Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, hematopoietic neoplasms like Leukemia, and solid tumors are some of the included conditions.
-
Medications
Different kind of medicines have also been reported in association with Multiple Change disease, top of the list are anti- inflammatory durgs like NSAIDs, Antibiotics like Ampicilline and Cefixime, others like Enalapril, Lithium, Interferon and Tamoxifen.
-
T cells abnormality
It has been postulated that a circulating factor produced by an abnormal clone of T cells directly inreasing glomerular filtration barrier permiability
-
Infections
Other possible cause of MCD is avariety of Infections, Examples are Syphilis, HIV, Mycoplasma, Echinococcus, and Ehrlichia.
-
Allergens
Commonly on Sting bee.
Diagnosis (Histology)
-
Renal Biopsy
To identify the underlying pathological lesion for resistant cases, mostly if sudden appearance of proteinuria and edema occurs.
-
Electron microscopy
Electron microscope is able to visualize typical abnormalities, it reveals fusion of epithelial cell of foot processes- a nonspecific finding seen in all form of Nephrotic syndrome. However, in light microscope the glomerulus usually appears normal
-
Urine test (Urinalysis)
To evaluate the amount of protein in the urine
-
24 hour urine collection
It is done to better quantify the amount of protein and creatinine in the urine
Treatment and Diet
-
Initial Therapy
Corticosteroids are the mainstay of initial therapy of MCD in adult patients. 90% of children respond in a period of 2 weeks of taking Corticosteroids like Prednisone. The medication is extended for another 6 weeks in lower doses. Adult response in medication is prolong compare to children. If steroid resistance happens or frequent relapse occur, a test of immunosuppressants is done.
The patients response can be categorized by the following:
1. Complete remission
Is described as the total resolution of proteinuria for atleast 3 to 5 consecutive days.
2. Partial remission
Is the lowering in the amount of proteinuria without complete clearing.
3. Relapse
Is defined as a the recurrence of proteinuria for atleast 3 to 5 consecutive days.
-
ACE Inhibitors or Angiotensin II receptor blockers
Used to treat hypertension and to reduce proteinuria, it can be combination or single only.
-
Warfarin
This is an initiated therapy for venous thrombosis
-
Loop Diuretics
This is an effective treatment of Edema.
-
Trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole
Used as prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii infection. Dapsone and Atovaquone is use as alternate for patients with allergy in sulfa containing antibiotics.
-
Supplements
Calcium and Vitamin D is also be considered to decrease the risk of osteoporosis due to prolonged steroid therapy.
-
Restriction in Sodium intake
To prevent water retention, control edema and prevent hypertension.
-
Protein intake
A moderate amount of protein in diet on accordance with Recommended daily allowance is needed.
Prognosis
The prognosis for Minimal change disease is extremely good in children and even in adults who have slower responses and markedly possible of therapy resistance. Early aggressive treatment for MCD demonstrates a reduced risk of complications of Nephrotic Syndrome such as infections, accelerated atherogenesis due to hyperlipidemia and thrombosis. The well described complication of MCD is Acute injury disease, however, it is comparatively uncommon.
In most number of MCD associated AKI cases, pathological diagnosis displays tubular necrosis. In advanced ages, Anti inflammatory medicines like NSAIDs and hypovolemia appear to be risk factors. Renal function usually recover after the occurrence of MCD associated AKI, but not always complete. Minimal change disease rarely progress to End stage renal disease. Death may still happen if disease complications occur.