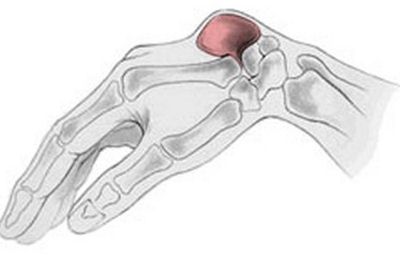
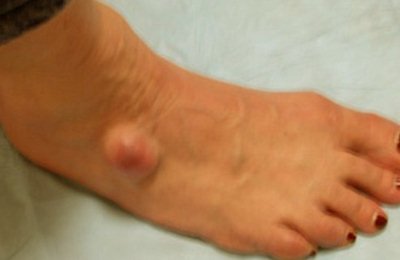
Ganglion Cyst – Pictures, Wrist, Foot, Treatment, Surgery Removal
What is a Ganglion Cyst?
We are living in a generation where cancer is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality; therefore, it is normal for us to panic whenever we notice any lump or tumor in our body. However, several lumps that occur are usually benign, like Ganglion cyst. Ganglion cysts, also known as Bible cysts, are a soft tissue mass in the joints.
How Ganglion Cyst formed?
A ganglion cyst can be described as a tumor or swelling on top of the joint or on the tendon itself. It appears like a sac of liquid which can be firm or spongy depending on the size. The liquid that fills the cyst is a sticky, thick, colorless, and jelly-like material. When the synovium in the surrounding tendon degenerates, the tendon sheath tends to buckle and weaken which causes the synovium to swell and form lumps.
Signs & Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of ganglion cyst include:
- Freely movable mass over a joint
- About 1-3 cm in size but may grow bigger
- Localized pain exacerbated by dorsiflexion of the wrist or moving the joint, but some cases are painless
- Swelling around the area which indicates compression of circulation
- Weakness or numbness on the distal portions such as the fingers which may indicate nerve compression
Characteristics
- Ganglion cyst is a type of completely harmless tumor.
- Ganglion cysts are more common in the female population.
- In addition, people between 20 – 60 years of age are more at risk for ganglion cysts, which accounts for seventy percent of cases.
- An individual can have one large cyst or multiple smaller cysts that arise from one cyst which project a grape-like appearance.
- Unlike cancerous tumors, ganglion cysts are mostly made up of soft tissues in the body and not toxins.
- Ganglion cysts are not malignant and do not spread to other areas of the body.
- Ganglion cyst may be painful and painless.
- Small lumps are usually painless, however as the size increases, it may compress some of the nerves and blood vessels and cause pain.
At Wrist, Foot & Ankle
Ganglion cysts are most likely to develop on the wrist joints, the back of the hand, and the anterior portion of the wrist. They can also develop on the knees, ankle, and top of the foot.
Ganglion cysts on the wrist, foot, and ankle arise from the accumulation of non-cancerous fluid which results to a palpable lump or tumors. These fluid-filled capsules have a tendency to increase in size, but they don’t have the ability to multiply. Although there are some cases of multiple cysts, it usually originates from a single main tumor.
Causes
The most common risk factor for ganglion cyst development is trauma.
Trauma
Ganglion cysts are commonly caused by trauma to the wrist tendon. After trauma, there could be a gradual or sudden onset of symptoms. Injury may involve blunt trauma to the area or repetitive movements such as frequent dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the wrists as seen in typists. Injury to the joint causes the synovial cavity to break which eventually leads to lump formation. Injury to the tendon covering may also cause tissues to bulge and form lumps.
Diagnosis
Every palpable lump or tumor in the body needs careful inspection and examination. Physical examination is done to assess the swelling and tenderness around the area. Definitive diagnosis involves excision of the cyst and submitting it for histological examination or biopsy to determine malignancy if any. Almost all of cases of ganglion cyst are benign.
Treatment Options
Ganglion cysts are managed primarily through removal of the lump. The following are possible methods of removing the ganglion cyst or relieving symptoms:
Surgery
Surgical removal of the ganglion cyst is the most common procedure to completely remove the cyst and prevent recurrence. The procedure involves minor operation to excise the cyst or cysts in the wrist. The excision also involves the removal of the cyst capsule to avoid new cysts from growing.
The procedure starts from injecting local anesthesia over the area to prevent pain sensation. Then, a small incision is made with the insertion of an arthroscope to visualize the inside portion of the joint. Upon confirming the location of the cyst, a small instrument is inserted to remove the lump.
The procedure is done in an out-patient setting and the surgical incision usually heals in a matter of one to two weeks.
Aspiration
Aspiration is a more conservative approach to ganglion cyst removal. The procedure involves splinting the wrist, followed by application of a local anesthetic. A small needle is inserted then the fluid is aspirated. Aspiration should be slow because sudden pulling of the plunger may cause further trauma inside the joint.
After aspiration, steroids are injected to prevent inflammation. Aspiration is effective in removing the cyst but recurrences are likely.
Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, naproxen and aspirin may be taken to reduce inflammation and pain.
Natural Remedies
Remedies may be instituted to decrease pain and inflammation. Warm compresses may be placed over the area for 15 minutes three times a day to relieve the condition.
Myths regarding management of ganglion cyst should be ignored because these may lead to further injury. Some people suggest the use of a Bible to smash the lump to be removed. Of course, this is a primitive practice which made ganglion cysts known as Bible cysts. Also, avoid self-pricking the lump to prevent infection.
Complications
Although ganglion cysts are benign, it may lead to possible complications which are usually not serious. Complications are often prevented through removal of the cysts that may be bothersome. Complications include:
Temporary loss of wrist function
Because of the swelling and nerve compression, the wrist may not be able to perform its functions, especially when the cysts grow big. Numbness and pain also result in poor movement of the hands and wrists.
Severe Pain
Significant pain may be experienced because of continued pressure on the nerves which stimulates nociception or pain sensation.
Infection
Infection may arise as a complication of ganglion excision. This may be prevented by ensuring aseptic technique throughout the surgery.
Prognosis
Since ganglion cysts are benign, there is a good prognosis. Surgical excision or aspiration of fluid can easily remove the cyst. Although chances of recurrence are high, patients should not worry because the recurrences are also benign. Recurrences are likely if the capsule that surrounds the cyst is not removed.
Prevention
Ganglion cysts may be prevented by avoiding excessive stress on the wrist joint. People should engage in an active range of motion exercises in a day to allow the circulation over the area. People who are likely to move the wrist most of the time for work, such as typists, construction workers and others, should ensure to rest the wrists after heavy work.
Ganglion Cysts Pictures
Pictures, photos, images of ganglion cyst at wrist, ankle and more.